Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the chemical reactions of those molecules. They are commonly found in biomolecules and extend off the carbon backbone, which is often represented by squiggly lines in structural formulas. Understanding these functional groups is essential as they play a crucial role in the structure and function of various biological molecules.
In biology, there are seven primary functional groups that are important to know:
The methyl group consists of a carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms (–CH3). This group is commonly found in lipids and plays a significant role in the structure of many organic compounds.
The hydroxyl group is characterized by an oxygen atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (–OH). This group is prevalent in alcohols and carbohydrates, influencing the solubility and reactivity of molecules.
The carbonyl group features a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O). This group is found in aldehydes and ketones, affecting the properties and reactivity of sugars and other biomolecules.
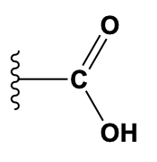
The carboxyl group combines the characteristics of both the carbonyl and hydroxyl groups, consisting of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and also bonded to a hydroxyl group (–COOH). This functional group is essential in amino acids and fatty acids, contributing to their acidic properties.
The amino group contains a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms (–NH2). This group is fundamental in amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, and plays a key role in the formation of peptide bonds.
The phosphate group is identified by the presence of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms (–PO43–). This group is critical in energy transfer through ATP and is a key component of nucleic acids.
Lastly, the sulfhydryl group consists of a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (–SH). This group is important in the structure of proteins, particularly in the formation of disulfide bonds that stabilize protein structure.
Familiarity with these functional groups will enhance your understanding of biomolecular interactions and reactions. As you progress in your studies, you may need to recognize their structures and functions, which will be vital for grasping more complex biological concepts.