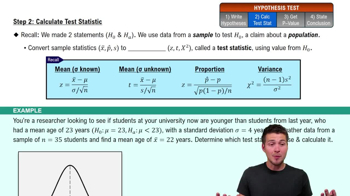
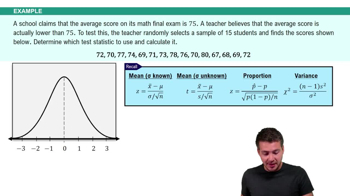
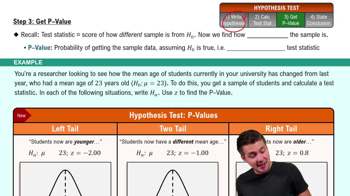
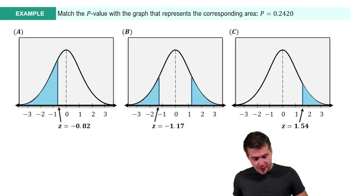
9. Hypothesis Testing for One Sample
Steps in Hypothesis Testing
Practice this topic
- Multiple Choice
A popular theme park claims that their weekly attendance is around . You believe that the weekly attendance is different than this claimed value, so you gather sample data. Write the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Multiple Choice
A candy manufacturer seeking to minimize the variation in weights of their candies claims to produce candies with a standard deviation less than g. Write the null and alternative hypotheses.
- Multiple Choice
A survey claimed that of adults prefer electric cars over traditional cars. A car manufacturer believes the true proportion is higher than . To test this, they survey a random sample of adults and find that say they prefer electric cars. Determine which test statistic to use & calculate it.
- Multiple Choice
Determine whether the hypothesis test is left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed.
- Textbook Question
Stem Cell Survey In a Newsweek poll of 882 adults, 481 (or 55%) said that they were in favor of using federal tax money to fund medical research using stem cells obtained from human embryos. A politician claims that people don’t really understand the stem cell issue and their responses to such questions are random responses equivalent to a coin toss. Use the following probabilities related to determining whether the result of 481 is significantly high (assuming the true rate is 50%). Is 481 significantly high? What should be concluded about the politician’s claim? Explain.
P(respondent says to use the federal tax money) = 0.5
P(among 882, exactly 481 says to use federal tax money) = 0.000713
P(among 882,481 or more say to use federal tax money) = 0.00389
- Textbook Question
Final Conclusions
In Exercises 21–24, use a significance level of α = 0.05 and use the given information for the following:
State a conclusion about the null hypothesis. (Reject H0 or fail to reject H0.)
Without using technical terms or symbols, state a final conclusion that addresses the original claim
Original claim: More than 35% of air travelers would choose another airline to have access to inflight Wi-Fi. The hypothesis test results in a P-value of 0.00001.
- Textbook Question
Final Conclusions
In Exercises 21–24, use a significance level of α = 0.05 and use the given information for the following:
State a conclusion about the null hypothesis. (Reject H0 or fail to reject H0.)
Without using technical terms or symbols, state a final conclusion that addresses the original claim.
Original claim: The mean pulse rate (in beats per minute) of adult males is 72 bpm. The hypothesis test results in a P-value of 0.0095.
- Textbook Question
Type I and Type II Errors
In Exercises 25–28, provide statements that identify the type I error and the type II error that correspond to the given claim. (Although conclusions are usually expressed in verbal form, the answers here can be expressed with statements that include symbolic expressions such as p = 0.1.)
The proportion of people who write with their left hand is equal to 0.1.