Back
BackProblem 3
A 6.0 m ✕ 12.0 m swimming pool slopes linearly from a 1.0 m depth at one end to a 3.0 m depth at the other. What is the mass of water in the pool?
Problem 4b
50 cm³ of gasoline are mixed with 50 cm³ of water. What is the average density of the mixture?
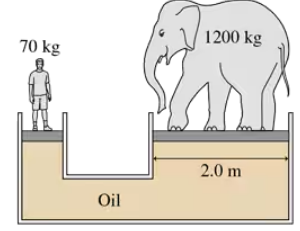
Problem 5
The deepest point in the ocean is 11 km below sea level, deeper than Mt. Everest is tall. What is the pressure in atmospheres at this depth?
Problem 6
A 1.0-m-diameter vat of liquid is 2.0 m deep. The pressure at the bottom of the vat is 1.3 atm. What is the mass of the liquid in the vat?
Problem 7a
What volume of water has the same mass as 8.0 m³ of ethyl alcohol?
Problem 11a
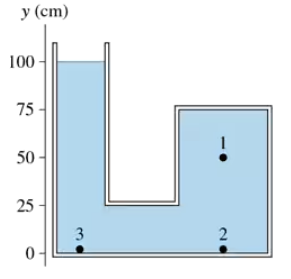
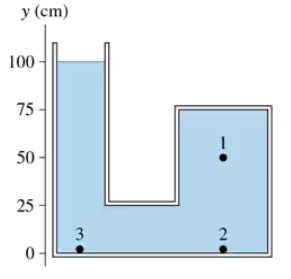
The container shown in FIGURE EX14.11 is filled with oil. It is open to the atmosphere on the left. What is the pressure at point 1?
Problem 11b
The container shown in FIGURE EX14.11 is filled with oil. It is open to the atmosphere on the left. What is the pressure difference between points 1 and 2? Between points 1 and 3?
Problem 12
What is the height of a water barometer at atmospheric pressure?
- What is the minimum hose diameter of an ideal vacuum cleaner that could lift a 10 kg (22 lb) dog off the floor?
Problem 14
Problem 15
A 6.00-cm-diameter sphere with a mass of 89.3 g is neutrally buoyant in a liquid. Identify the liquid.
Problem 16
A 2.0 cm ✕ 2.0 cm ✕ 6.0 cm block floats in water with its long axis vertical. The length of the block above water is 2.0 cm. What is the block's mass density?
Problem 19
What is the tension of the string in FIGURE EX14.19?
Problem 23
Styrofoam has a density of 150 kg/m³. What is the maximum mass that can hang without sinking from a 50-cm-diameter Styrofoam sphere in water? Assume the volume of the mass is negligible compared to that of the sphere.
Problem 28
What does the top pressure gauge read in FIGURE EX14.28?
Problem 29a
A 2.0 mL syringe has an inner diameter of 6.0 mm, a needle inner diameter of 0.25 mm, and a plunger pad diameter (where you place your finger) of 1.2 cm. A nurse uses the syringe to inject medicine into a patient whose blood pressure is 140/100. What is the minimum force the nurse needs to apply to the syringe?
Problem 29b
A 2.0 mL syringe has an inner diameter of 6.0 mm, a needle inner diameter of 0.25 mm, and a plunger pad diameter (where you place your finger) of 1.2 cm. A nurse uses the syringe to inject medicine into a patient whose blood pressure is 140/100. The nurse empties the syringe in 2.0 s. What is the flow speed of the medicine through the needle?
Problem 32
An unknown liquid flows smoothly through a 6.0-mm-diameter horizontal tube where the pressure gradient is 600 Pa/m. Then the tube diameter gradually shrinks to 3.0 mm. What is the pressure gradient in this narrower portion of the tube?
Problem 39
A 5.0-m-diameter solid aluminum sphere is launched into space. By how much does its diameter increase? Give your answer in μm.
Problem 42
A friend asks you how much pressure is in your car tires. You know that the tire manufacturer recommends 30 psi, but it's been a while since you've checked. You can't find a tire gauge in the car, but you do find the owner's manual and a ruler. Fortunately, you've just finished taking physics, so you tell your friend, 'I don't know, but I can figure it out.' From the owner's manual you find that the car's mass is 1500 kg. It seems reasonable to assume that each tire supports one-fourth of the weight. With the ruler you find that the tires are 15 cm wide and the flattened segment of the tire in contact with the road is 13 cm long. What answer—in psi—will you give your friend?
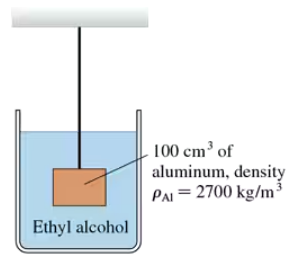
Problem 43b
When a second student joins the first, the piston sinks. What is the second student's mass?
Problem 44
A 55 kg cheerleader uses an oil-filled hydraulic lift to hold four 110 kg football players at a height of 1.0 m. If her piston is 16 cm in diameter, what is the diameter of the football players' piston?
Problem 46
Glycerin is poured into an open U-shaped tube until the height in both sides is 20 cm. Ethyl alcohol is then poured into one arm until the height of the alcohol column is 20 cm. The two liquids do not mix. What is the difference in height between the top surface of the glycerin and the top surface of the alcohol?
Problem 47b
An aquarium of length L, width (front to back) W, and depth D is filled to the top with liquid of density ρ. Find an expression for the force of the liquid on the front window of the aquarium.
Problem 48b
It's possible to use the ideal-gas law to show that the density of the earth's atmosphere decreases exponentially with height. That is, ρ = ρ₀ exp (-z/z₀), where z is the height above sea level, ρ₀ is the density at sea level (you can use the Table 14.1 value), and z₀ is called the scale height of the atmosphere. What is the density of the air in Denver, at an elevation of 1600 m? What percent of sea-level density is this?
Problem 49
The average density of the body of a fish is 1080 kg/m³ . To keep from sinking, a fish increases its volume by inflating an internal air bladder, known as a swim bladder, with air. By what percent must the fish increase its volume to be neutrally buoyant in fresh water? The density of air at 20°C is 119 kg/m³.
Problem 52
One day when you come into physics lab you find several plastic hemispheres floating like boats in a tank of fresh water. Each lab group is challenged to determine the heaviest rock that can be placed in the bottom of a plastic boat without sinking it. You get one try. Sinking the boat gets you no points, and the maximum number of points goes to the group that can place the heaviest rock without sinking. You begin by measuring one of the hemispheres, finding that it has a mass of 21 g and a diameter of 8.0 cm. What is the mass of the heaviest rock that, in perfectly still water, won't sink the plastic boat?
Problem 56
A nuclear power plant draws 3.0 x 106 L/min of cooling water from the ocean. If the water is drawn in through two parallel, 3.0-m-diameter pipes, what is the water speed in each pipe?
Problem 57a
A nonviscous liquid of density p flows at speed v₀ through a horizontal pipe that expands smoothly from diameter d₀ to a larger diameter d₁. The pressure in the narrower section is p₀. Find an expression for the pressure p₁ in the wider section.
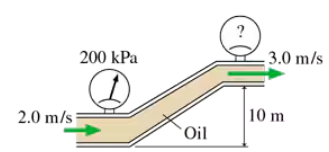
Problem 57b
A pressure gauge reads 50 kPa as water flows at 10.0 m/s through a 16.8-cm-diameter horizontal pipe. What is the reading of a pressure gauge after the pipe has expanded to 20.0 cm in diameter?
Problem 58
A tree loses water to the air by the process of transpiration at the rate of 110 g/h. This water is replaced by the upward flow of sap through vessels in the trunk. If the trunk contains 2000 vessels, each 100 μm in diameter, what is the upward speed in mm/s of the sap in each vessel? The density of tree sap is 1040 kg/m³.