Back
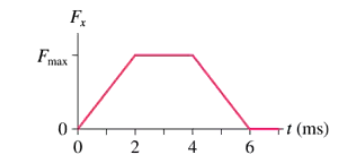
BackProblem 40
A 60 g tennis ball with an initial speed of 32 m/s hits a wall and rebounds with the same speed. FIGURE P11.40 shows the force of the wall on the ball during the collision. What is the value of Fmax , the maximum value of the contact force during the collision?
Problem 43
A particle of mass m is at rest at t = 0. Its momentum for t > 0 is given by px = 6t² kg m/s, where t is in s. Find an expression for Fx (t), the force exerted on the particle as a function of time.
Problem 45b
Most geologists believe that the dinosaurs became extinct 65 million years ago when a large comet or asteroid struck the earth, throwing up so much dust that the sun was blocked out for a period of many months. Suppose an asteroid with a diameter of 2.0 km and a mass of 1.0×10¹³ kg hits the earth (6.0×10²⁴ kg) with an impact speed of 4.0×10⁴ m/s. What percentage is this of the earth's speed around the sun? The earth orbits the sun at a distance of 1.5×10¹¹ m .
Problem 47
BIO Squids rely on jet propulsion to move around. A 1.50 kg squid (including the mass of water inside the squid) drifting at 0.40 m/s suddenly ejects 0.100 kg of water to get itself moving at 2.50 m/s . If drag is ignored over the small interval of time needed to expel the water (the impulse approximation), what is the water’s ejection speed relative to the squid?
Problem 49a
A bullet of mass m is fired into a block of mass M that is at rest. The block, with the bullet embedded, slides distance d across a horizontal surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction is μk .Find an expression for the bullet's speed vbullet.
Problem 49b
What is the speed of a 10g bullet that, when fired into a 10kg stationary wood block, causes the block to slide 5.0 cm across a wood table?
Problem 51
An object at rest on a flat, horizontal surface explodes into two fragments, one seven times as massive as the other. The heavier fragment slides 8.2 m before stopping. How far does the lighter fragment slide? Assume that both fragments have the same coefficient of kinetic friction.
Problem 53
A 1500 kg weather rocket accelerates upward at 10 m/s². It explodes 2.0 s after liftoff and breaks into two fragments, one twice as massive as the other. Photos reveal that the lighter fragment traveled straight up and reached a maximum height of 530 m. What were the speed and direction of the heavier fragment just after the explosion?
Problem 54
Two 500 g blocks of wood are 2.0 m apart on a frictionless table. A 10 g bullet is fired at 400 m/s toward the blocks. It passes all the way through the first block, then embeds itself in the second block. The speed of the first block immediately afterward is 6.0 m/s . What is the speed of the second block after the bullet stops in it?
Problem 59
The stoplight had just changed and a 2000 kg Cadillac had entered the intersection, heading north at 3.0 m/s , when it was struck by a 1000 kg eastbound Volkswagen. The cars stuck together and slid to a halt, leaving skid marks angled 35° north of east. How fast was the Volkswagen going just before the impact?
Problem 61
A 500 g particle has velocity vx = −5.0 m/s at t = −2 s. Force Fx = (4−t2) N, where t is in s, is exerted on the particle between t = −2 s and t = 2 s. This force increases from 0 N at t = −2 s to 4 N at t = 0 s and then back to 0 N at t = 2 s. What is the particle's velocity at t = 2s?
Problem 62
A 30 ton rail car and a 90 ton rail car, initially at rest, are connected together with a giant but massless compressed spring between them. When released, the 30 ton car is pushed away at a speed of 4.0 m/s relative to the 90 ton car. What is the speed of the 30 ton car relative to the ground?
Problem 64a
A 100 g ball moving to the right at 4.0 m/s collides head-on with a 200g ball that is moving to the left at 3.0 m/s. If the collision is perfectly elastic, what are the speed and direction of each ball after the collision?
Problem 65
One end of a massless, 30-cm-long spring with spring constant 15 N/m is attached to a 250 g stationary air-track glider; the other end is attached to the track. A 500 g glider hits and sticks to the 250 g glider, compressing the spring to a minimum length of 22 cm. What was the speed of the 500 g glider just before impact?
Problem 66
Consider a partially elastic collision in which ball A of mass m with initial velocity (vix)A collides with stationary ball B, also of mass m, and in which 1/4 of the mechanical energy is dissipated as thermal energy. Find expressions for the final velocities of each ball. Hint: Mathematically there are two solutions; however, one of them is physically impossible.
Problem 68
The nucleus of the polonium isotope ²¹⁴Po (mass 214 u) is radioactive and decays by emitting an alpha particle (a helium nucleus with mass 4 u). Laboratory experiments measure the speed of the alpha particle to be 1.92×10⁷ m/s . Assuming the polonium nucleus was initially at rest, what is the recoil speed of the nucleus that remains after the decay?
Problem 69c
A neutron is an electrically neutral subatomic particle with a mass just slightly greater than that of a proton. A free neutron is radioactive and decays after a few minutes into other subatomic particles. In one experiment, a neutron at rest was observed to decay into a proton (mass 1.67×10-27 kg) and an electron (mass 9.11×10-31 kg) . The proton and electron were shot out back-to-back. The proton speed was measured to be 1.0 ×105 m/s, and the electron speed was 3.0×107 m/s. No other decay products were detected. How much momentum did this neutrino 'carry away' with it?
Problem 70
A 45 g projectile explodes into three pieces: a 20 g piece with velocity 25 î m/s, a 15 g piece with velocity −10 î + 10 ĵ m/s, and a 10 g piece with velocity −15 î − 20 ĵ m/s. What was the projectile's velocity just before the explosion?
Problem 71b
A white ball traveling at 2.0 m/s hits an equal-mass red ball at rest. The white ball is deflected by 25° and slowed to 1.5 m/s. What percentage of the initial mechanical energy is lost in the collision?
Problem 73
A 2100 kg truck is traveling east through an intersection at 2.0 m/s when it is hit simultaneously from the side and the rear. (Some people have all the luck!) One car is a 1200 kg compact traveling north at 5.0 m/s. The other is a 1500 kg midsize traveling east at 10 m/s. The three vehicles become entangled and slide as one body. What are their speed and direction just after the collision?
Problem 79a
In Problems and you are given the equation(s) used to solve a problem. For each of these, you are to write a realistic problem for which this is the correct equation(s).
Problem 79b
In Problems and you are given the equation(s) used to solve a problem. For each of these, you are to finish the solution of the problem, including a pictorial representation.
Problem 80
A spaceship of mass 2.0×10⁶ kg is cruising at a speed of 5.0×10⁶ m/s when the antimatter reactor fails, blowing the ship into three pieces. One section, having a mass of 5.0×10⁵ kg, is blown straight backward with a speed of 2.0×10⁶ m/s . A second piece, with mass 8.0×10⁵ kg, continues forward at 1.0×10⁶ m/s. What are the direction and speed of the third piece?
Problem 81
A 1000 kg cart is rolling to the right at 5.0 m/s. A 70 kg man is standing on the right end of the cart. What is the speed of the cart if the man suddenly starts running to the left with a speed of 10 m/s relative to the cart?
Problem 82
A 20 kg wood ball hangs from a 2.0-m-long wire. The maximum tension the wire can withstand without breaking is 400 N. A 1.0 kg projectile traveling horizontally hits and embeds itself in the wood ball. What is the greatest speed this projectile can have without causing the wire to break?
Problem 85b
A rocket with a total mass of 330,000 kg when fully loaded burns all 280,000 kg of fuel in 250 s. The engines generate 4.1 MN of thrust. What is this rocket's speed at the instant all the fuel has been burned if it is launched in deep space? If it is launched vertically from the earth?