Back
BackProblem 1a
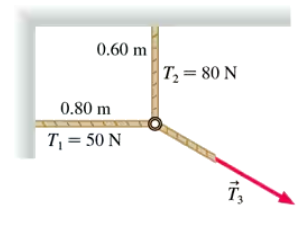
The three ropes in FIGURE EX6.1 are tied to a small, very light ring. Two of these ropes are anchored to walls at right angles with the tensions shown in the figure. What are the magnitude and direction of the tension T3 in the third rope?
Problem 5
A football coach sits on a sled while two of his players build their strength by dragging the sled across the field with ropes. The friction force on the sled is 1000 N, the players have equal pulls, and the angle between the two ropes is 20°. How hard must each player pull to drag the coach at a steady 2.0 m/s?
Problem 6a
In an electricity experiment, a 1.0 g plastic ball is suspended on a 60-cm-long string and given an electric charge. A charged rod brought near the ball exerts a horizontal electrical force Felectric on it, causing the ball to swing out to a 20° angle and remain there. What is the magnitude of Felectric?
Problem 9
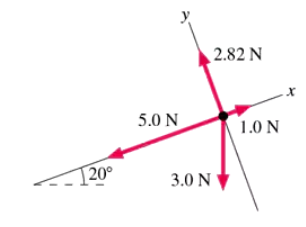
The forces in FIGURE EX6.9 act on a 2.0 kg object. What are the values of ax and ay, the x- and y-components of the object's acceleration?
Problem 10
FIGURE EX6.10 shows the force acting on a 2.0 kg object as it moves along the x-axis. The object is at rest at the origin at t = 0 s. What are its acceleration and velocity at t = 6 s?
Problem 12b
A horizontal rope is tied to a 50 kg box on frictionless ice. What is the tension in the rope if: The box moves at a steady 5.0 m/s?
Problem 13b
A 50 kg box hangs from a rope. What is the tension in the rope if: The box moves up at a steady 5.0 m/s?
Problem 13c
A 50 kg box hangs from a rope. What is the tension in the rope if: The box has vy = 5.0 m/s and is speeding up at 5.0 m/s2
Problem 16b
The position of a 2.0 kg mass is given by x = (2t3 - 3t2) where t is in seconds. What is the net horizontal force on the mass at t = 1s?
Problem 17a
A woman has a mass of 55 kg. What is her weight while standing on earth?
Problem 18a
It takes the elevator in a skyscraper 4.0 s to reach its cruising speed of 10 m/s. A 60 kg passenger gets aboard on the ground floor. What is the passenger's weight before the elevator starts moving?
Problem 18c
It takes the elevator in a skyscraper 4.0 s to reach its cruising speed of 10 m/s. A 60 kg passenger gets aboard on the ground floor. What is the passenger's weight after the elevator reaches its cruising speed?
Problem 19
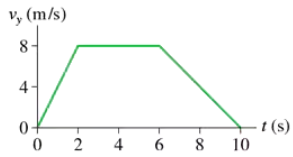
FIGURE EX6.19 shows the velocity graph of a 75 kg passenger in an elevator. What is the passenger's weight at t=1s? At 5 s? At 9 s?
Problem 20a
Zach, whose mass is 80 kg, is in an elevator descending at 10 m/s. The elevator takes 3.0 s to brake to a stop at the first floor. What is Zach's weight before the elevator starts braking?
Problem 21a
A 20,000 kg rocket has a rocket motor that generates 3.0 x 105 N of thrust. Assume no air resistance. What is the rocket's initial upward acceleration?
Problem 23
The mass of the sun is 2.0 x 1030 kg. A 5.0 x 1014 kg comet is 75 million kilometers from the sun. What is the magnitude of the comet's acceleration toward the sun?
Problem 25
Bonnie and Clyde are sliding a 300 kg bank safe across the floor to their getaway car. The safe slides with a constant speed if Clyde pushes from behind with 385 N of force while Bonnie pulls forward on a rope with 350 N of force. What is the safe's coefficient of kinetic friction on the bank floor?
Problem 26b
A 10 kg crate is placed on a horizontal conveyor belt. The materials are such that = 0.5 and = 0.3. Draw a free-body diagram showing all the forces on the crate if the conveyer belt is speeding up.
Problem 27
Bob is pulling a 30 kg filing cabinet with a force of 200 N, but the filing cabinet refuses to move. The coefficient of static friction between the filing cabinet and the floor is 0.80. What is the magnitude of the friction force on the filing cabinet?
Problem 28
A 4000 kg truck is parked on a 15° slope. How big is the friction force on the truck? The coefficient of static friction between the tires and the road is 0.90.
Problem 29
A rubber-wheeled 50 kg cart rolls down a 15° concrete incline. What is the magnitude of the cart's acceleration if rolling friction is (a) neglected and (b) included?
Problem 30
A 50,000 kg locomotive is traveling at 10 m/s when its engine and brakes both fail. How far will the locomotive roll before it comes to a stop? Assume the track is level.
Problem 31
A 1500 kg car skids to a halt on a wet road where = 0.50. How fast was the car traveling if it leaves 65-m-long skid marks?
Problem 33a
Above what speed does a 3.0-mm-diameter ball bearing in 20°C water experience quadratic drag?
Problem 33b
Below what speed does a 3.0-mm-diameter ball bearing in 20°C air experience linear drag?
Problem 34
A medium-sized jet has a 3.8-m-diameter fuselage and a loaded mass of 85,000 kg. The drag on an airplane is primarily due to the cylindrical fuselage, and aerodynamic shaping gives it a drag coefficient of 0.37. How much thrust must the jet's engines provide to cruise at 230 m/s at an altitude where the air density is 1.0 kg/m3
Problem 35a
So-called volcanic 'ash' is actually finely pulverized rock blown high into the atmosphere. A typical ash particle is a 50-μm-diameter piece of silica with a density of 2400 kg/m3. How long would it take this ash particle to fall from a height of 5.0 km in vacuum?
Problem 35b
So-called volcanic 'ash' is actually finely pulverized rock blown high into the atmosphere. A typical ash particle is a 50--diameter piece of silica with a density of 2400 kg/m3. How long in hours does it take this ash particle to fall from a height of 5.0 km in still air? Use the properties of 20°C air at sea level.
Problem 37
An E. coli bacterium can be modeled as a 0.50 μm diameter sphere that has the density of water. Rotating flagella propel a bacterium through 40°C water with a force of 65 fN, where 1 fN = 1femtonewton = 10-15 N. What is the bacterium's speed in μm/s?
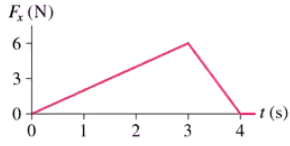
Problem 38
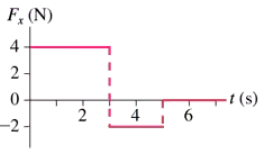
A 2.0 kg object initially at rest at the origin is subjected to the time-varying force shown in FIGURE P6.38. What is the object's velocity at t = 4 s?