Back
BackProblem 1
What voltage will produce 0.25 A of current through a 5400-Ω resistor?
Problem 1a
Calculate the terminal voltage for a battery with an internal resistance of 0.900 Ω and an emf of 6.00 V when the battery is connected in series with a 61.0-Ω resistor.
Problem 7
(a) What is the current in the 13-Ω heating element of a 240-V clothes dryer?
(b) How much charge passes through the element in 15 min? (Assume direct current.)
Problem 8b
A 12-V battery causes a current of 0.50 A through a resistor. How many joules of energy does the battery lose in a minute?
Problem 10
A 4.5-V battery is connected to a bulb whose resistance is 2.3 Ω. How many electrons leave the battery per minute?
Problem 15
Neglect the internal resistance of a battery unless the problem refers to it. Ten 7.0-W Christmas tree lights are connected in series to each other and to a 120-V source. What is the resistance of each bulb?
Problem 21
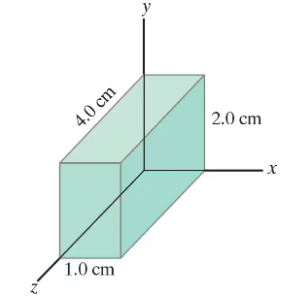
A rectangular solid made of carbon has sides of lengths 1.0 cm, 2.0 cm, and 4.0 cm, lying along the x, y, and z axes, respectively (Fig. 25–36). Determine the resistance for current that passes through the solid in the y direction, (Assume the resistivity is ρ = 3.0 x 10⁻⁵ Ω•m).
Problem 26
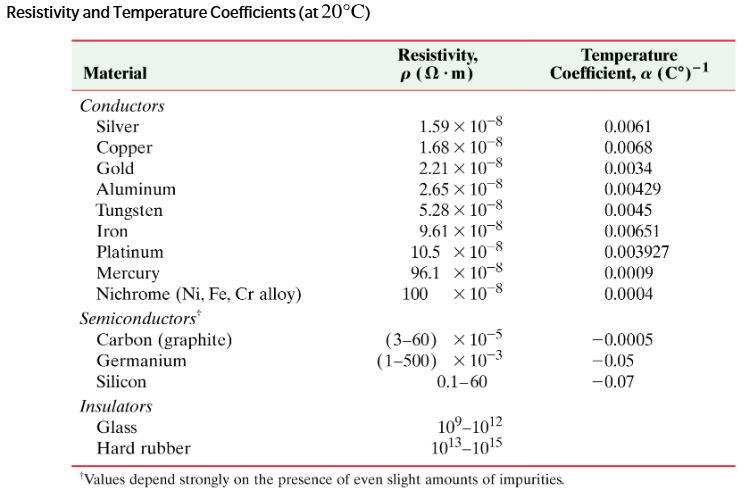
The filament of an incandescent lightbulb has a resistance of 12 Ω at 20°C and 140 Ω when hot.
(a) Calculate the temperature of the filament when it is hot, and take into account the change in length and area of the filament due to thermal expansion (assume tungsten for which the thermal expansion coefficient is ≈ 5.5 10⁻⁶ C°⁻¹ ).
(b) In this temperature range, what is the percentage change in resistance due to thermal expansion, and what is the percentage change in resistance due solely to the change in ρ? Use Eq. 25–5.
Problem 29
The heating element of an electric oven is designed to produce 3.1 kW of heat when connected to a 240-V source. What must be the resistance of the element?
Problem 31
An electric car uses a 45-kW (160-hp) motor. If the battery pack is designed for 340 V, what current would the motor need to draw from the battery? Neglect any energy losses in getting energy from the battery to the motor.
Problem 35
You buy a 75-W lightbulb in Europe, where electricity is delivered at 240 V. If you use the bulb in the United States at 120 V (assume its resistance does not change), how bright will it be relative to 75-W 120-V bulbs? [Hint: Assume roughly that brightness is proportional to power consumed.]
Problem 37
At $0.12/kWh, what does it cost to leave a 25-W porch light on day and night for a year?
Problem 39
A flashlight uses two AA 1.5-V batteries connected in series to provide 3.0 V across the bulb, as in Fig. 25–4b. The bulb draws 135 mA when turned on.
(a) Calculate the resistance of the bulb and the power dissipated.
(b) By what factor would the power increase if four AA batteries in series (total 6.0 V) were used with the same bulb? (Neglect heating effects of the filament.) Why shouldn’t you try this?
Problem 41
(II) A power station delivers 750 kW of power at 12,000 V to a factory through wires with total resistance 3.0 Ω. How much less power is wasted if the electricity is delivered at 50,000 V rather than 12,000 V?
Problem 46
Calculate the peak current in a 2.5-k Ω resistor connected to a 220-V rms ac source.
Problem 52b
Determine the maximum current passing through a 2.7-hp pump connected to a 240-Vrms ac power source.
Problem 54b
A heater coil connected to a 240-Vᵣₘₛ ac line has a resistance of 32Ω. What are the maximum and minimum values of the instantaneous power?
Problem 55b
A 0.65-mm-diameter copper wire carries a tiny current of 3.2 μA. Estimate the current density.
Problem 55c
A 0.65-mm-diameter copper wire carries a tiny current of 3.2 μA. Estimate the electric field in the wire.
Problem 62
What is the average current drawn by a 1.0-hp 120-V motor? (1 hp = 746 W.)
Problem 74a
A microwave oven running at 72% efficiency delivers 950 W to the interior. Find the power drawn from the source.
Problem 78b
A 2800-W oven is connected to a 240-V source. How long will it take to bring 150 mL of 15°C water to 100°C assuming 65% efficiency?
Problem 81b
Suppose a current is given by the equation I = 1.40 sin 210t, where I is in amperes and t in seconds. What is the rms value of the current?
Problem 82
A 100-W, 120-V incandescent lightbulb has a resistance of 12 Ω when cold (20°C) and 150 Ω when on (hot). Calculate its power consumption (a) at the instant it is turned on, and (b) after a few moments when it is hot.
Problem 86a
Lightbulb A is rated at 120 V and 40 W for household applications. Lightbulb B is rated at 12 V and 40 W for automotive applications. What is the current through each bulb?
Problem 86b
Lightbulb A is rated at 120 V and 40 W for household applications. Lightbulb B is rated at 12 V and 40 W for automotive applications. What is the resistance of each bulb?
Problem 90a
Copper wire of diameter 0.259 cm is used to connect a set of appliances at 120 V, which draw 1250 W of power total. What power is wasted in 25.0 m of this wire?
Problem 92
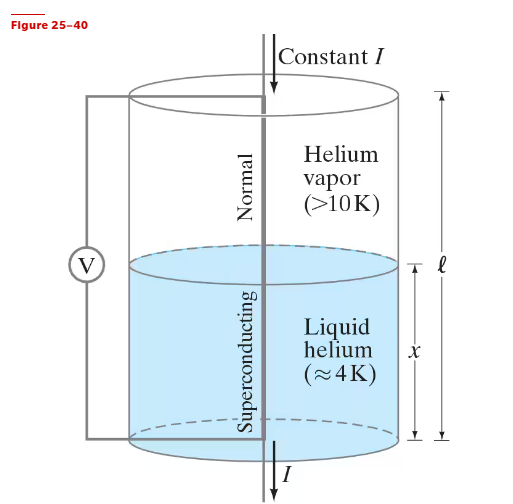
The level of liquid helium (temperature ≈ 4K) in its storage tank can be monitored using a vertically aligned niobium–titanium (NbTi) wire, whose length ℓ spans the height of the tank. In this level-sensing setup, an electronic circuit maintains a constant electrical current I at all times in the NbTi wire and a voltmeter monitors the voltage V across this wire. The NbTi wire is superconducting ( R = 0) if below its transition temperature of 10 K, so the portion of the wire immersed in the liquid helium is in the superconducting state, while the portion above the liquid (in helium vapor with temperature above 10 K) is in the normal state. Define ƒ = x/ℓ to be the fraction of the tank filled with liquid helium (Fig. 25–40) and V₀ to be the value of the voltage V when the tank is empty (ƒ = 0) . Determine the relation between f and V (in terms of V₀).
Problem 95b
Household wiring has sometimes used aluminium instead of copper.Typical copper wire used for home wiring in the U.S. has a diameter of 1.63 mm. What is the resistance of 125 m of this wire?
Problem 95c
Household wiring has sometimes used aluminium instead of copper. What would be the resistance of the same wire if it were made of aluminum?