Back
Back Giancoli Douglas 5th edition
Giancoli Douglas 5th edition Ch. 17 - Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and the Ideal Gas Law
Ch. 17 - Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and the Ideal Gas LawProblem 3a
(I) (a) “Room temperature” is often taken to be 68°F. What is this on the Celsius scale?
Problem 5
A thermometer tells you that you have a fever of 38.5°C. What is this in Fahrenheit?
Problem 7b
In an alcohol-in-glass thermometer, the alcohol column has length 12.61 cm at 0.0°C and length 22.79 cm at 100.0°C. What is the temperature if the column has length 14.40 cm?
Problem 9
The Eiffel Tower (Fig. 17–20) is built of wrought iron approximately 300 m tall. Estimate how much its height changes between January (average temperature of 2°C) and July (average temperature of 25°C). Ignore the angles of the iron beams and treat the tower as a vertical beam.
<IMAGE>
Problem 11a
The density of water at 4°C is 1.00 x 10³ kg / m³. What is water’s density at 94°C? Assume a constant coefficient of volume expansion.
Problem 14
At a given latitude, ocean water in the so-called mixed layer (from the surface to a depth of about 50 m) is at approximately the same temperature due to the mixing action of waves. Assume that because of global warming, the temperature of the mixed layer is everywhere increased by 0.5°C, while the temperature of the deeper portions of the ocean remains unchanged. Estimate the resulting rise in sea level. The ocean covers about 70% of the Earth’s surface.
Problem 15
An aluminum sphere is 8.75 cm in diameter. What will be its % change in volume if it is heated from 30°C to 140°C?
Problem 16a
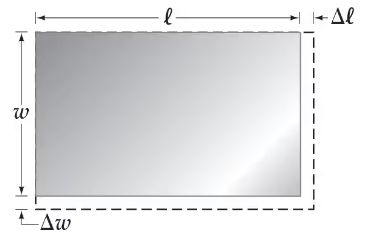
A uniform rectangular plate of length ℓ and width ω has a coefficient of linear expansion α. Show that, if we neglect very small quantities, the change in area of the plate due to a temperature change ∆T is ∆A = 2αℓω ∆T. See Fig. 17–21.
Problem 17
A glass is filled to the brim with 450.0 mL of water, all at 100.0°C. If the temperature of glass and water is decreased to 20.0°C, how much water could be added to the glass?
Problem 19
It is observed that 55.50 mL of water at 20°C completely fills a container to the brim. When the container and the water are heated to 60°C, 0.35 g of water is lost.
(a) What is the coefficient of volume expansion of the container?
(b) What is the most likely material of the container? Density of water at 60°C is 0.98324 g/mL.
Problem 20
A brass plug is to be placed in a ring made of iron. At 15°C, the diameter of the plug is 8.756 cm and that of the inside of the ring is 8.742 cm. They must both be brought to what common temperature in order to fit?
Problem 21
If a fluid is contained in a long narrow vessel so it can expand in essentially one direction only, show that the effective coefficient of linear expansion α is approximately equal to the coefficient of volume expansion β.
Problem 23a
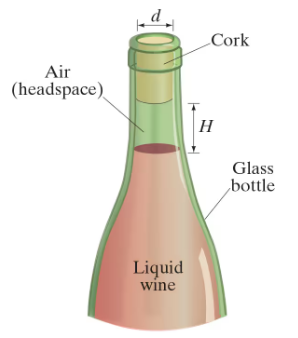
Wine bottles are never completely filled: a small volume of air is left in the glass bottle’s cylindrically shaped neck (inner diameter d = 18.5 mm) to allow for wine’s fairly large coefficient of thermal expansion. The distance H between the surface of the liquid contents and the bottom of the cork is called the “headspace height” (Fig. 17–22), and is typically H = 1.5 cm for a 750-mL bottle filled at 20°C. Due to its alcoholic content, wine’s coefficient of volume expansion is about double that of water; in comparison, the thermal expansion of glass can be neglected. Estimate H if the bottle is kept at 10°C.
Problem 24a
Determine a formula for the change in surface area of a uniform solid sphere of radius r if its coefficient of linear expansion is α (assumed constant) and its temperature is changed by ∆T.
Problem 25
The pendulum in a grandfather clock is made of brass and keeps perfect time at 17°C. How much time is gained or lost in a year if the clock is kept at 26°C? (Assume the frequency dependence on length for a simple pendulum applies; see Chapter 14.)
Problem 26
Water’s coefficient of volume expansion in the temperature range from 0°C to about 20°C is given approximately by β = α + bT + cT² , with α = - 6.43 x 10⁻⁵ (C°)⁻¹ , b = 1.70 x 10⁻⁵ (C°)⁻² , and c = -2.02 x 10⁻⁷ ((C°)⁻³. Using the formula for density from Problem 22, show that water has its greatest density at approximately 4.0°C.
Problem 27
An aluminum bar has the desired length when at 12°C. How much stress is required to keep it at this length if the temperature increases to 38°C? [See Table 12–1.]
Problem 28b
A horizontal steel I-beam of a cross-sectional area of 0.041 m² is rigidly connected to two fixed vertical supports. If the beam was installed when the temperature was 25°C, is the ultimate strength of the steel exceeded?
Problem 36
If 12.50 mol of helium gas is at 10.0°C and a gauge pressure of 0.350 atm, calculate
(a) the volume of the helium gas under these conditions and
(b) the temperature if the gas is compressed to precisely half the volume at a gauge pressure of 1.00 atm.
Problem 39a
A storage tank at STP contains 26.5 kg of nitrogen (N₂). What is the volume of the tank?
Problem 41
What is the pressure inside a 41.0-L container holding 105.0 kg of argon gas at 21.6°C?
Problem 43
A sealed metal container contains a gas at 30.0°C and absolute pressure 1.00 atm. To what temperature must the gas be heated for the pressure to double to 2.00 atm? (Ignore expansion of the container.)
Problem 45
If 59.2 L of oxygen at 18.0°C and an absolute pressure of 2.45 atm are compressed to 38.8 L and at the same time the temperature is raised to 56.0°C, what will the new pressure be?
Problem 46
A helium-filled balloon escapes a child’s hand at sea level and 20.0°C. When it reaches an altitude of 3600 m, where the temperature is 5.0°C and the pressure only 0.64 atm, how will its volume compare to that at sea level?
Problem 48
A helium balloon rises because of a buoyant force. By what percentage does the buoyant force on a helium balloon change if the temperature of the helium is increased from 15°C to 25°C while the temperature of the surrounding air is unchanged? Assume that the pressure of the helium remains constant.
Problem 50
You buy an “airtight” potato chip bag packaged at sea level, and take the chips on an airplane flight. When you take the potato chip bag out of your “carry-on” bag, you notice it has noticeably “puffed up.” Airplane cabins are typically pressurized at 0.75 atm, and assuming the temperature inside an airplane is about the same as inside a potato chip processing plant, by what percentage has the bag “puffed up” in comparison to when it was packaged?
Problem 55
An air bubble at the bottom of a lake 32.0 m deep has a volume of 1.00 cm³ . If the temperature at the bottom is 5.5°C and at the top 18.5°C, what is the radius of the bubble just before it reaches the surface?
Problem 57
How many moles of water are there in 1.00 L at STP? How many molecules?
Problem 67b
A precise steel tape measure has been calibrated at 14°C. At 37°C, what will be the percentage error?
Problem 72a
Use the ideal gas law to show that, for an ideal gas at constant pressure, the coefficient of volume expansion is equal to β = 1/ T, where T is the kelvin temperature. Compare to Table 17–1 for gases at T = 293 K.