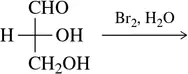Back
BackProblem 32b
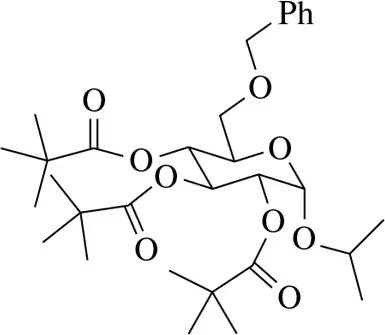
Suggest a synthesis of the following acylated sugars.
(b)
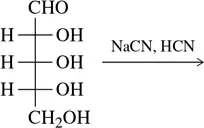
Problem 34b
Predict the product of each of the following reactions.
(b)
Problem 34c
Predict the product of each of the following reactions.
(c)
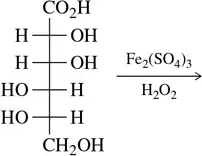
Problem 34d
Predict the product of each of the following reactions.
(d)
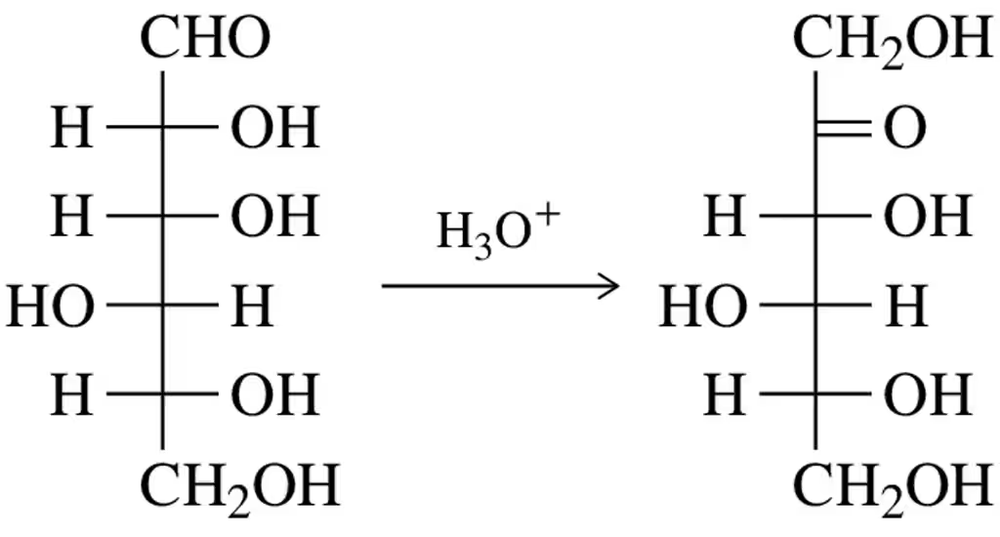
Problem 36
Ketohexoses form from aldohexoses. Suggest a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed version of this reaction. What type of reaction is this? [You’ve seen it before.]
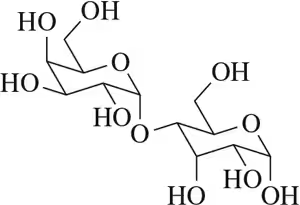
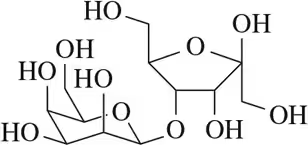
Problem 39a
In each of the disaccharides shown (a–c), (i) identify the reducing end of the sugar, (ii) tell what monosaccharides are used to make it, and (iii) tell what type of glycoside linkage is present.
(a)
Problem 39b
In each of the disaccharides shown (a–c), (i) identify the reducing end of the sugar, (ii) tell what monosaccharides are used to make it, and (iii) tell what type of glycoside linkage is present.
(b)
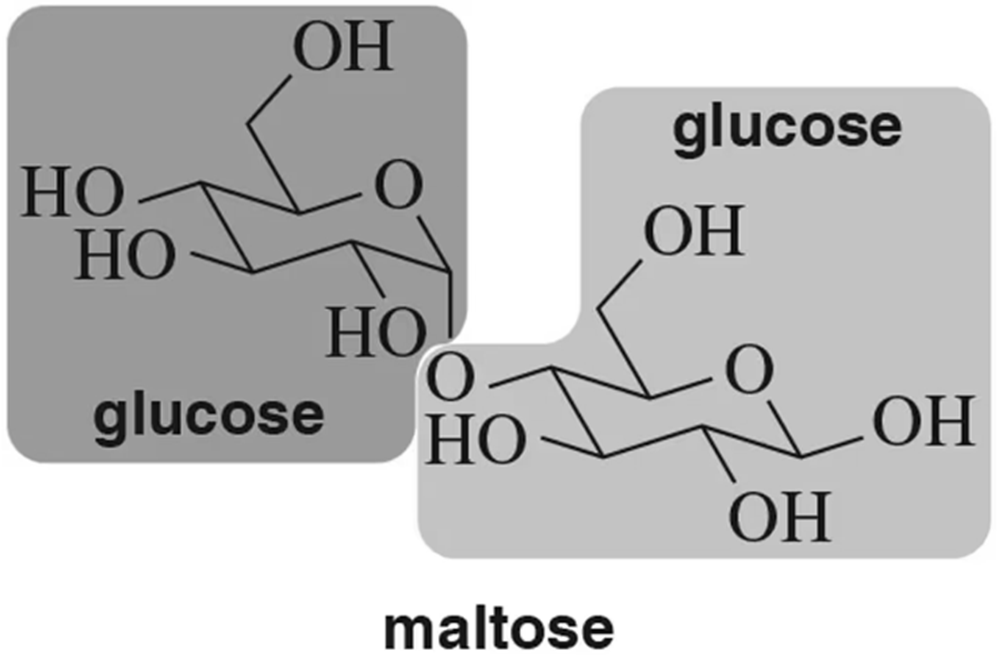
Problem 40
Maltose, like cellobiose, is composed of two glucose units. What is the difference between maltose and cellobiose?
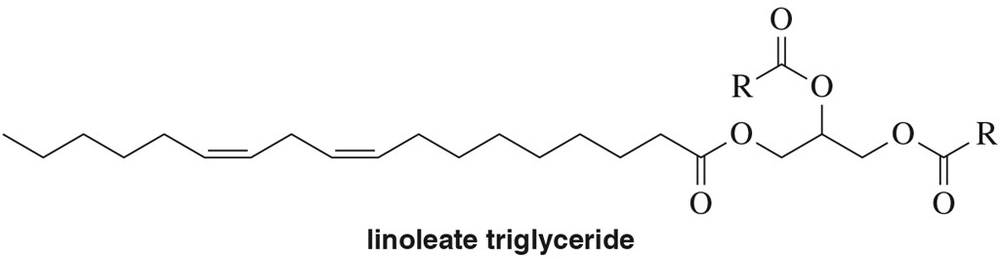
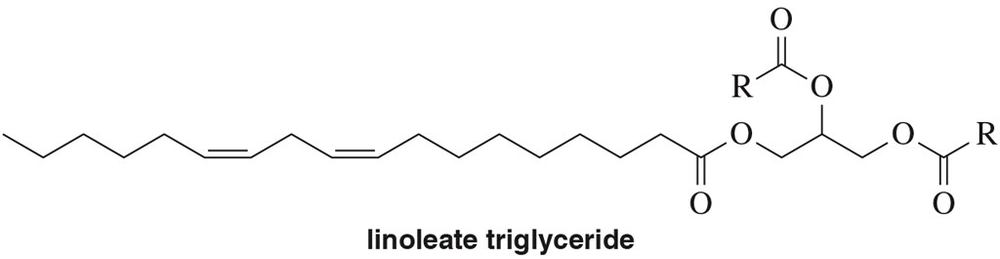
Problem 59a
Identify the product when each of the following reactions is performed on the triglyceride of linoleic acid (linoleate).
(a) H2 , Pd
Problem 59b
Identify the product when each of the following reactions is performed on the triglyceride of linoleic acid (linoleate).
(b) H2 , Ni (partial hydrogenation)
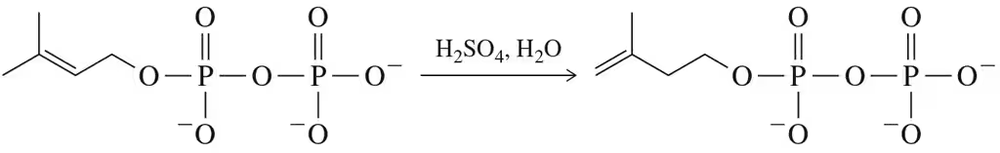
Problem 60
Draw a mechanism for the acid-catalyzed, nonenzymatic conversion of DPP to IPP. How do you know your mechanism is correct?
Problem 62a
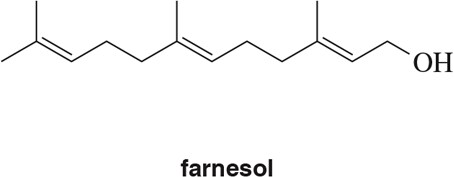
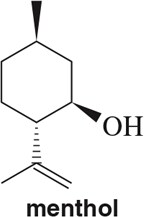
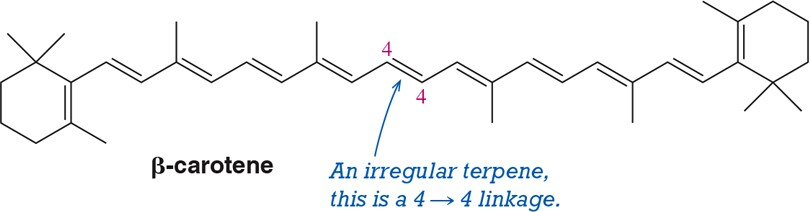
Identify the isoprene units in the terpenes shown. In cross-linked or ring-containing terpenes, linkages can be formed between more than just C1 and C4 of isoprene.
(a)
Problem 62b
Identify the isoprene units in the terpenes shown. In cross-linked or ring-containing terpenes, linkages can be formed between more than just C1 and C4 of isoprene.
(b)
Problem 62c
Identify the isoprene units in the terpenes shown. In cross-linked or ring-containing terpenes, linkages can be formed between more than just C1 and C4 of isoprene.
(c)
Problem 62e
Identify the isoprene units in the terpenes shown. In cross-linked or ring-containing terpenes, linkages can be formed between more than just C1 and C4 of isoprene.
(e)
Problem 65
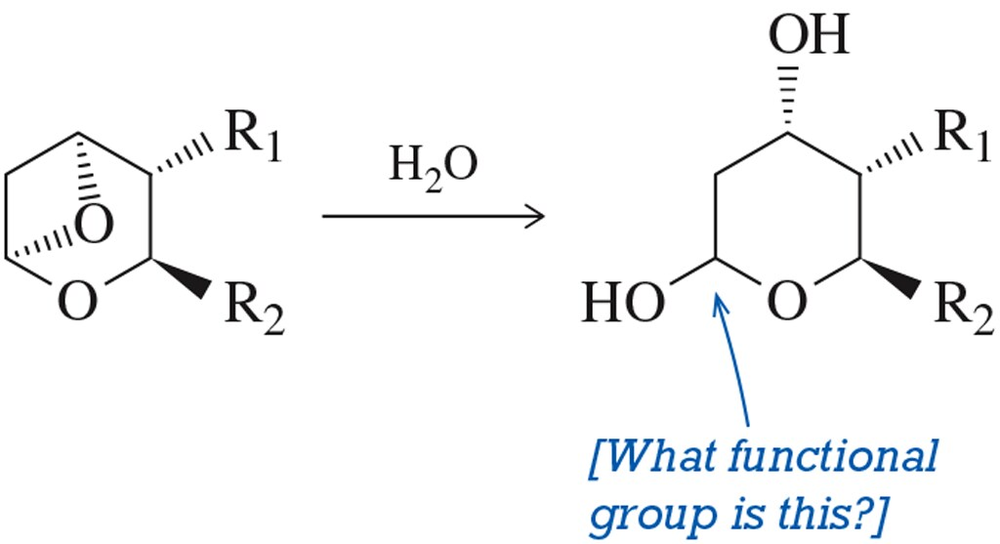
Suggest a mechanism by which TXB2 might be formed from TXA2 in an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction. [The structure has been simplified.]
Problem 67
Starting with a Fischer projection of d-glucose (and other sugars), switch only the stereocenter that gave it the designation of d. What new sugar have you made? [Hint: The answer is not l-glucose.]
Problem 68
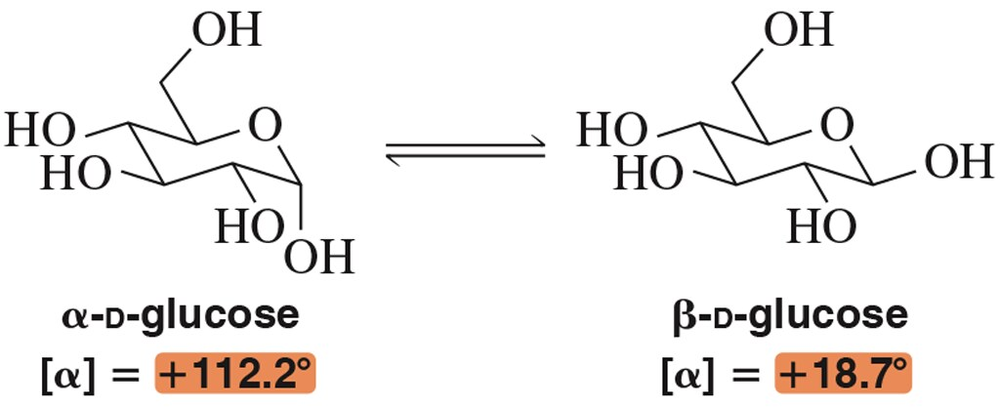
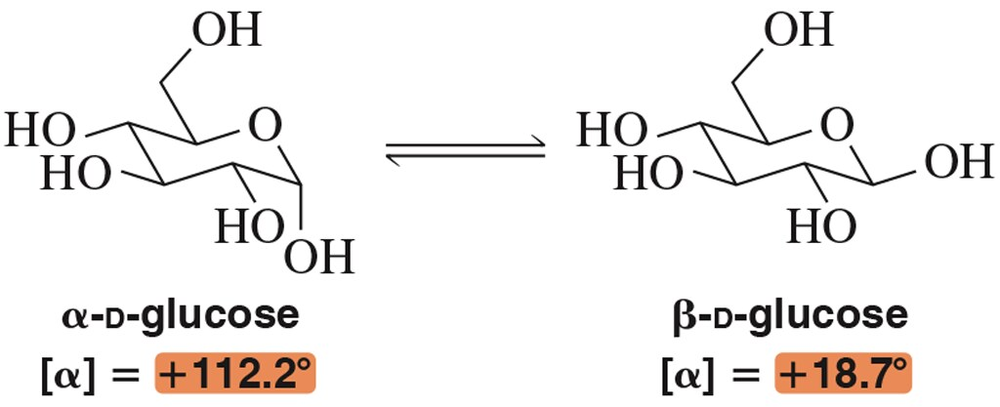
The α- and β-anomers of glucose are shown here. In solution, these two epimers can interconvert through a process called mutarotation.
Given that α-D-glucose has a specific rotation of + 112.2° , why is the specific rotation of β-D-glucose not -112.2°? What molecule would have a specific rotation of -112.2°?
Problem 69
Upon dissolving α-D-glucose or β-D-glucose in water, the specific rotation gradually changes, eventually reaching +52.6° for both solutions. Explain what is happening here.
Problem 70
The α- and β-anomers of glucose are shown here.
In solution, these two epimers can interconvert through a process called mutarotation. What is the ratio of anomers (α:β) when the specific rotation is +52.6°
Problem 72
(a) Suggest an arrow-pushing mechanism for the mutarotation of α-d-glucose to β-d-glucose in the presence of acid. Acid isn’t necessary, but it does increase the rate of the process.
(b) What is the role of acid in your mechanism?
Problem 77
Is the compound d or l?
Problem 80
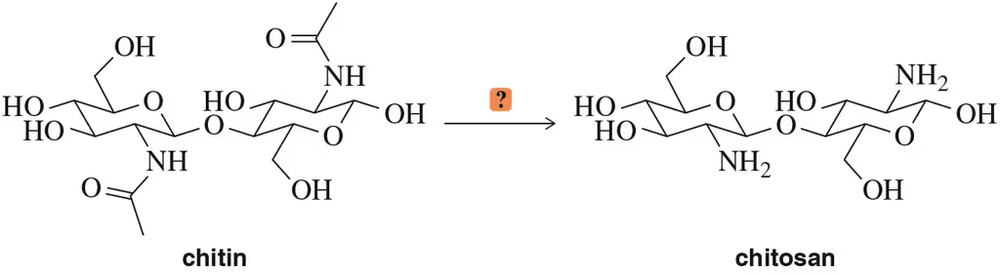
A derivative of chitin, called chitosan, is sometimes incorporated into bandages to aid healing. Propose a reaction to convert the chitin dimer into a chitosan dimer. [Note: The glycoside linkage is unstable in acid.]
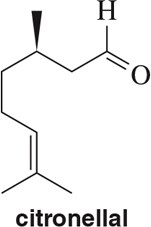
Problem 90
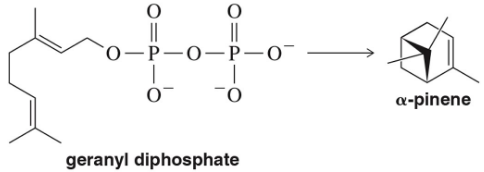
α-Pinene is a terpene found in pine trees. Starting from geranyl diphosphate (a terpene), draw the arrow-pushing mechanism to produce α-pinene. Assume that an enzyme active site will provide whatever acids and bases you might need.