15. Analytical Techniques:IR, NMR, Mass Spect
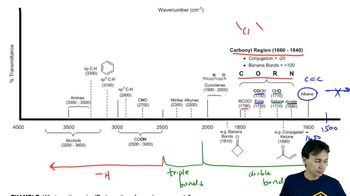
Infrared Spectroscopy Table
Practice this topic
- Open Question
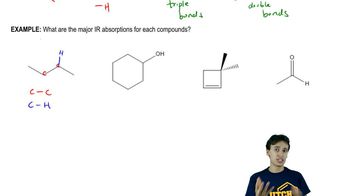
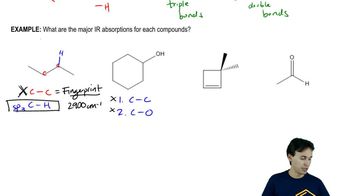
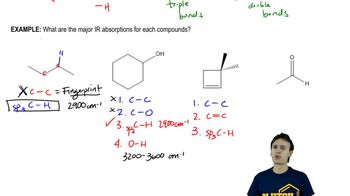
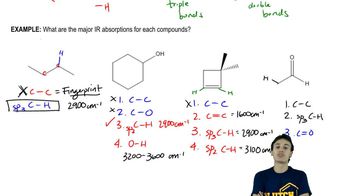
Answer each of the following questions based on the images below.
a) Which compounds show an intense peak ~ 1700 cm-1?
b) Which compound shows an intense, broad peak at ~ 3400 cm-1?
c) Which compound has a peak at ~1700 cm-1, but no peaks at 2700 cm-1?
d) Which compound has no signal beyond the fingerprint region?
- Multiple Choice
Identify which carbonyl group will exhibit a signal at a lower wavenumber
- Multiple ChoiceWhich molecule would you expect tohave the lowest wavenumber for the C=O π bond IR band?
- Multiple ChoiceAn IR spectrum has bands at ~ 2100 cm−1 and ~ 3300 cm−1. What functional group does this molecule likely represent?
- Textbook Question
The infrared spectra for three compounds are provided. Each compound has one or more of the following functional groups: conjugated ketone, ester, amide, nitrile, and alkyne. Determine the functional group(s) in each compound, and assign the major peaks above 1600 cm–1.
<IMAGE>
- Textbook Question
Spectra are given for three compounds. Each compound has one or more of the following functional groups: alcohol, amine, ketone, aldehyde, and carboxylic acid. Determine the functional group(s) in each compound, and assign the major peaks above 1600 cm–1.
<IMAGE>
- Textbook Question
A common lab experiment is the dehydration of cyclohexanol to cyclohexene.
(a) Explain how you could tell from the IR spectrum whether your product was pure cyclohexene, pure cyclohexanol, or a mixture of cyclohexene and cyclohexanol. Give approximate frequencies for distinctive peaks.
(b) Explain why mass spectrometry might not be a good way to distinguish cyclohexene from cyclohexanol.