Back
BackProblem 1
Which of the following is not a distinguishing characteristic of prokaryotic cells?
a. They usually have a single, circular chromosome.
b. They have 70S ribosomes.
c. They have cell walls containing peptidoglycan.
d. Their DNA is not associated with histones.
e. They lack a plasma membrane.
Problem 1
Diagram each of the following flagellar arrangements:
a. Lophotrichous
b. Monotrichous
c. Peritrichous
d. Amphitrichous
e. Polar
Problem 2
Use the following choices to answer the following question.
a. No change will result; the solution is isotonic.
b. Water will move into the cell.
c. Water will move out of the cell.
d. The cell will undergo osmotic lysis.
e. Sucrose will move into the cell from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
Which statement best describes what happens when a gram-positive bacterium is placed in distilled water and penicillin?
Problem 2
Endospore formation is called (a) ________. It is initiated by (b) ________. Formation of a new cell from an endospore is called (c) ________. This process is triggered by (d) ________.
Problem 3
Draw the bacterial shapes listed in (a), (b), and (c). Then draw the shapes in (d), (e), and (f), showing how they are special conditions of a, b, and c, respectively.
a. Spiral
b. Bacillus
c. Coccus
d. Spirochetes
e. Staphylococci
f. Streptobacilli
Problem 3
Use the following choices to answer the following question.
a. No change will result; the solution is isotonic.
b. Water will move into the cell.
c. Water will move out of the cell.
d. The cell will undergo osmotic lysis.
e. Sucrose will move into the cell from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
Which statement best describes what happens when a gram-negative bacterium is placed in distilled water and penicillin?
Problem 4
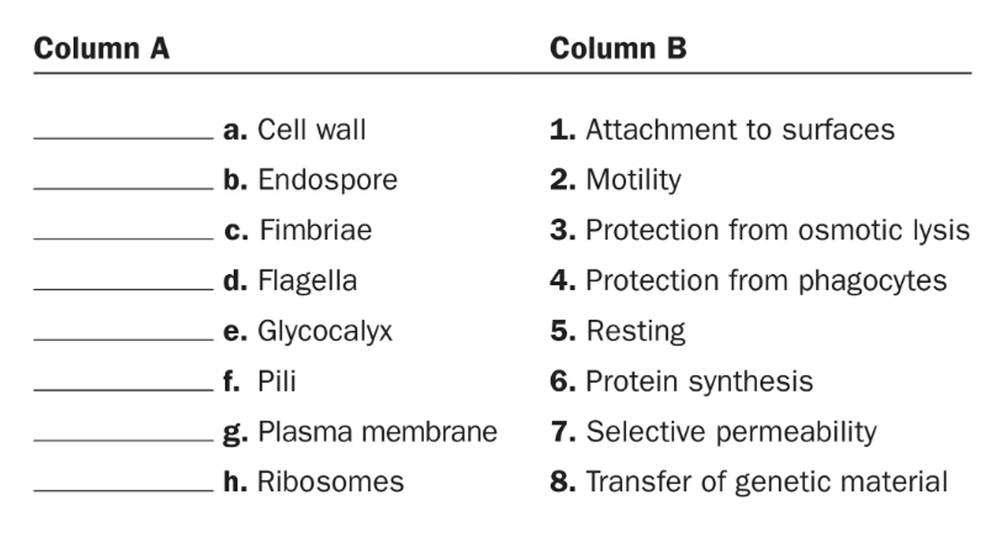
Match the structures in column A to their functions in column B.
Problem 4
Use the following choices to answer the following question.
a. No change will result; the solution is isotonic.
b. Water will move into the cell.
c. Water will move out of the cell.
d. The cell will undergo osmotic lysis.
e. Sucrose will move into the cell from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
Which statement best describes what happens when a gram-positive bacterium is placed in an aqueous solution of lysozyme and 10% sucrose?
Problem 5
Why is an endospore called a resting structure? Of what advantage is an endospore to a bacterial cell?
Problem 5
Which of the following statements best describes what happens to a cell exposed to polymyxins that destroy phospholipids?
a. In an isotonic solution, nothing will happen.
b. In a hypotonic solution, the cell will lyse.
c. Water will move into the cell.
d. Intracellular contents will leak from the cell.
e. Any of the above might happen.
Problem 6
Compare and contrast the following:
a. Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion
b. Active transport and facilitated diffusion
c. Active transport and group translocation
Problem 6
Which of the following is false about fimbriae?
a. They are composed of protein.
b. They may be used for attachment.
c. They are found on gram-negative cells.
d. They are composed of pilin.
e. They may be used for motility.
Problem 7
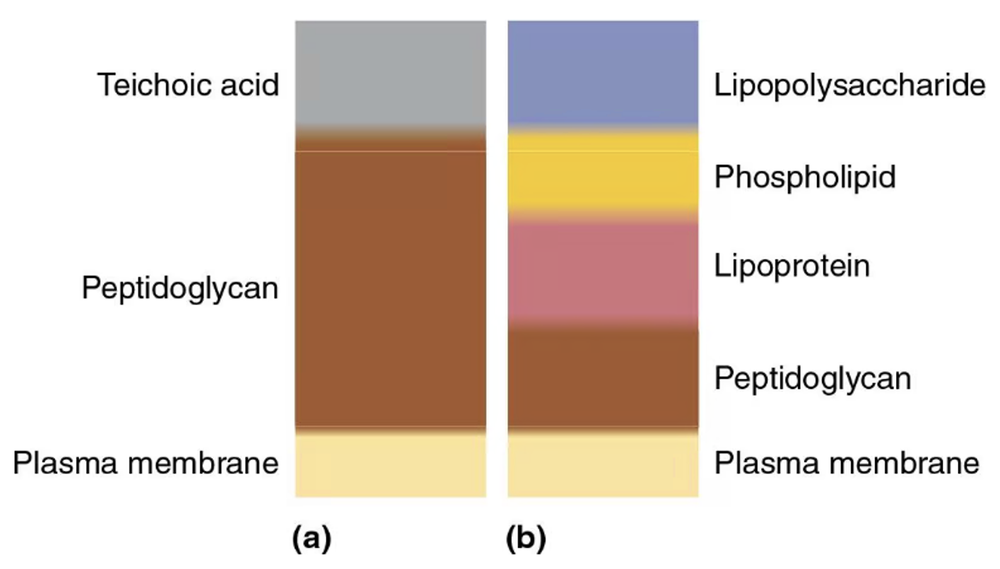
Answer the following questions using the diagrams provided, which represent cross sections of bacterial cell walls.
a. Which diagram represents a gram-positive bacterium? How can you tell?
b. Explain how the Gram stain works to distinguish these two types of cell walls.
c. Why does penicillin have no effect on most gram-negative cells?
d. How do essential molecules enter cells through each wall?
e. Which cell wall is toxic to humans?
Problem 7
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
a. Glycocalyx—adherence
b. Pili—reproduction
c. Cell wall—toxin
d. Cell wall—protection
e. Plasma membrane—transport
Problem 8
Which of the following pairs is mismatched?
a. Metachromatic granules—stored phosphates
b. Polysaccharide granules—stored starch
c. Lipid inclusions—poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid
d. Sulfur granules—energy reserve
e. Ribosomes—protein storage
Problem 8
Starch is readily metabolized by many cells, but a starch molecule is too large to cross the plasma membrane. How does a cell obtain the glucose molecules from a starch polymer? How does the cell transport these glucose molecules across the plasma membrane?
Problem 9
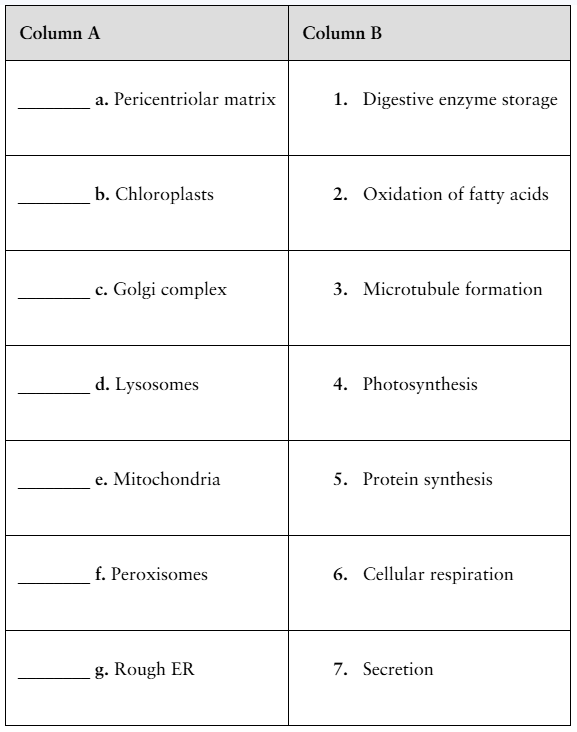
Match the characteristics of eukaryotic cells in column A with their functions in column B.
Problem 9
You have isolated a motile, gram-positive cell with no visible nucleus. You can assume this cell has
a. Ribosomes.
b. Mitochondria.
c. An endoplasmic reticulum.
d. A Golgi complex.
e. All of the above
Problem 10
The antibiotic amphotericin B disrupts plasma membranes by combining with sterols; it will affect all of the following cells except
a. Animal cells.
b. Gram-negative bacterial cells.
c. Fungal cells.
d. Mycoplasma cells.
e. Plant cells.
Problem 10
What group of microbes is characterized by cells that form filaments, reproduce by spores, and have peptidoglycan in their cell walls?
Problem 28.5a
Use the following choices to answer questions 3–5:
a. Bacillus coagulans
b. Byssochlamys
c. flat sour spoilage
d. Lactobacillus
e. thermophilic anaerobic spoilage
A heat-resistant fungus that causes spoilage in acidic foods.