Back
BackProblem 1
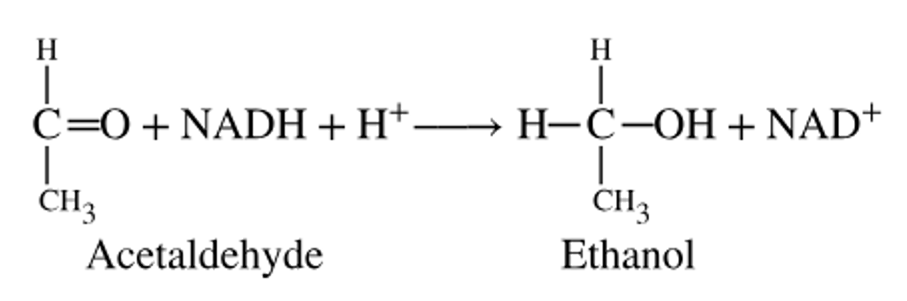
Which substance in the following reaction is being reduced?
a. Acetaldehyde
b. NADH
c. Ethanol
d. NAD+
Problem 1
Use the following diagrams (a), (b), and (c) for the question.
<IMAGE>
Name pathways diagrammed in parts (a), (b), and (c) of the figure.
a. Show where glycerol is catabolized and where fatty acids are catabolized.
b. Show where glutamic acid (an amino acid) is catabolized:
<IMAGE>
c. Show how these pathways are related.
d. Where is ATP required in pathways (a) and (b)?
e. Where is CO₂ released in pathways (b) and (c)?
f. Show where a long-chain hydrocarbon such as petroleum is catabolized.
g. Where is NADH (or FADH₂ or NADPH) used and produced in these pathways?
h. Identify four places where anabolic and catabolic pathways are integrated.
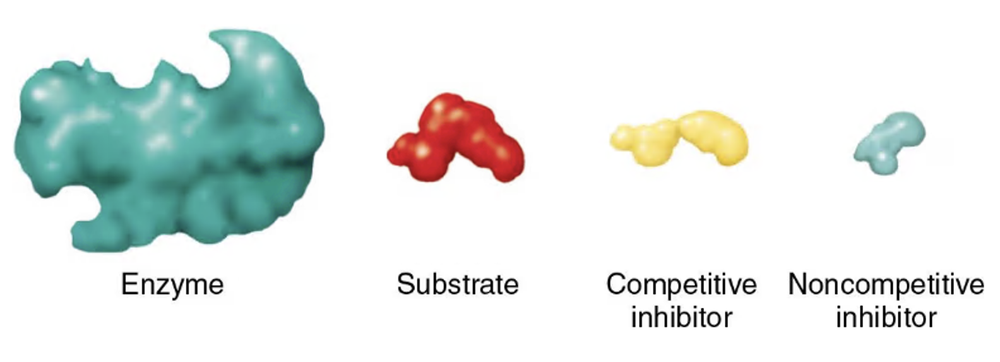
Problem 2
Using the following diagrams, show each of the following:
a. where the substrate will bind
b. where the competitive inhibitor will bind
c. where the noncompetitive inhibitor will bind
d. which of the four elements could be the inhibitor in feedback inhibition
e. What effect will the reactions in (a), (b), and (c) have?
Problem 2
Which of the following reactions produces the most molecules of ATP during aerobic metabolism?
a. Glucose → Glucose 6-phosphate
b. Phosphoenolpyruvic acid → Pyruvic acid
c. Glucose → Pyruvic acid
d. Acetyl CoA → CO2 + H2O
e. Succinic acid → Fumaric acid
Problem 3
Which of the following processes does not generate ATP?
a. Photophosphorylation
b. The Calvin-Benson cycle
c. Oxidative phosphorylation
d. Substrate-level phosphorylation
e. All of the above generate ATP
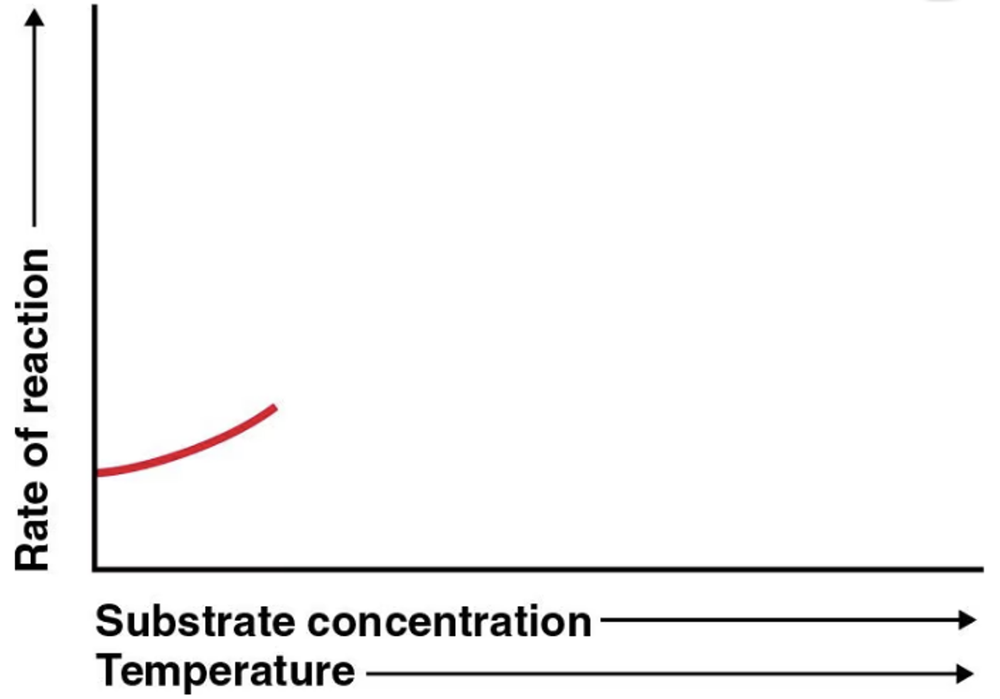
Problem 3
An enzyme and substrate are combined. The rate of reaction begins as shown in the following graph. To complete the graph, show the effect of increasing substrate concentration on a constant enzyme concentration. Show the effect of increasing temperature.
Problem 4
Which of the following compounds has the greatest amount of energy for a cell?
a. CO2
b. ATP
c. glucose
d. O2
e. lactic acid
Problem 4
Define oxidation-reduction, and differentiate the following terms:
a. Aerobic and anaerobic respiration
b. Respiration and fermentation
c. Cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation
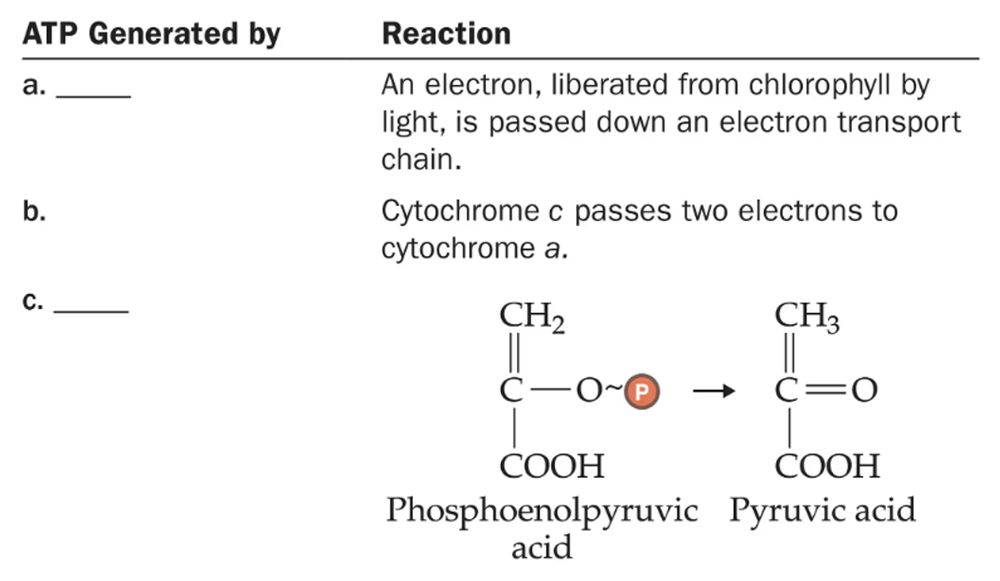
Problem 5
There are three mechanisms for the phosphorylation of ADP to produce ATP. Write the name of the mechanism that describes each of the reactions in the following table.
Problem 5
Which of the following is the best definition of the Krebs cycle?
a. The oxidation of pyruvic acid
b. The way cells produce CO2
c. A series of chemical reactions in which NADH is produced from the oxidation of pyruvic acid
d. A method of producing ATP by phosphorylating ADP
e. A series of chemical reactions in which ATP is produced from the oxidation of pyruvic acid
Problem 6
All of the energy-producing biochemical reactions that occur in cells, such as photophosphorylation and glycolysis, are ________ reactions.
Problem 6
Which of the following is the best definition of cellular respiration?
a. A sequence of redox reactions with O2 as the final electron acceptor
b. A sequence of redox reactions with the final electron acceptor from the environment
c. A method of generating ATP
d. The complete oxidation of glucose to CO2 and H2O
e. A series of reactions in which pyruvic acid is oxidized to CO2 and H2O
Problem 7
Use the following choices to answer the question.
a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ with O2 for 5 days
b. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ without O2 for 5 days
c. Both a and b
d. Neither a nor b
Which culture produces the most lactic acid?
Problem 7
Fill in the following table with the carbon source and energy source of each type of organism.
Problem 8
Write your own definition of the chemiosmotic mechanism of ATP generation. On Figure 5.16, mark the following using the appropriate letter:
a. The acidic side of the membrane
b. The side with a positive electrical charge
c. Potential energy
d. Kinetic energy
Problem 8
Use the following choices to answer the question.
a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ with O2 for 5 days
b. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ without O2 for 5 days
c. Both a and b
d. Neither a nor b
Which culture produces the most ATP?
Problem 9
Why must NADH be reoxidized? How does this happen in an organism that uses respiration? Fermentation?
Problem 9
Use the following choices to answer the question.
a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ with O2 for 5 days
b. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ without O2 for 5 days
c. Both a and b
d. Neither a nor b
Which culture uses NAD+ ?
Problem 10
What nutritional type is a colorless microbe that uses the Calvin-Benson cycle, uses H₂ as the electron donor to its ETC, and uses elemental S as the final electron acceptor in the ETC?
Problem 10
Use the following choices to answer the question.
a. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ with O2 for 5 days
b. E. coli growing in glucose broth at 35℃ without O2 for 5 days
c. Both a and b
d. Neither a nor b
Which culture uses the most glucose?