Back
BackProblem 1
Match the following choices to questions 1–4:
a. Innate resistance
b. Naturally acquired active immunity
c. Naturally acquired passive immunity
d. Artificially acquired active immunity
e. Artificially acquired passive immunity
The type of protection provided by the injection of diphtheria toxoid.
Problem 1
Contrast the terms in the following pairs:
a. Innate and adaptive immunity
b. Humoral and cellular immunity
c. Active and passive immunity
d. TH1 and TH2 cells
e. Natural and artificial immunity
f. T-dependent and T-independent antigens
g. Immunoglobulin and TCR
Problem 2
What does MHC stand for? What is the function of MHC? What types of T cells interact with MHC class I? With MHC class II?
Problem 2
Match the following choices to questions 1–4:
a. Innate resistance
b. Naturally acquired active immunity
c. Naturally acquired passive immunity
d. Artificially acquired active immunity
e. Artificially acquired passive immunity
The type of protection resulting from recovery from an infection.
Problem 3
Match the following choices to questions 1–4:
a. Innate resistance
b. Naturally acquired active immunity
c. Naturally acquired passive immunity
d. Artificially acquired active immunity
e. Artificially acquired passive immunity
The type of protection resulting from recovery from an infection.
Problem 3
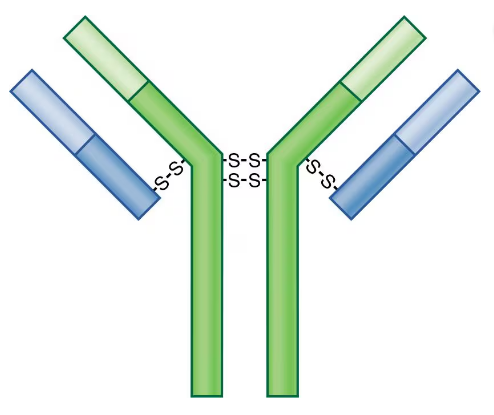
Label the heavy chains, light chains, and variable and Fc regions of this typical antibody. Indicate where the antibody binds to antigen. Sketch an IgM antibody.
Problem 4
Diagram the roles that T cells and B cells play in immunity.
Problem 4
Match the following choices to questions 1–4:
a. Innate resistance
b. Naturally acquired active immunity
c. Naturally acquired passive immunity
d. Artificially acquired active immunity
e. Artificially acquired passive immunity
A newborn’s immunity to yellow fever.
Problem 5
Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
Antibodies that protect the fetus and newborn.
Problem 5
Explain a function for the following types of cells: CTL, TH, and Treg. What is a cytokine?
Problem 6
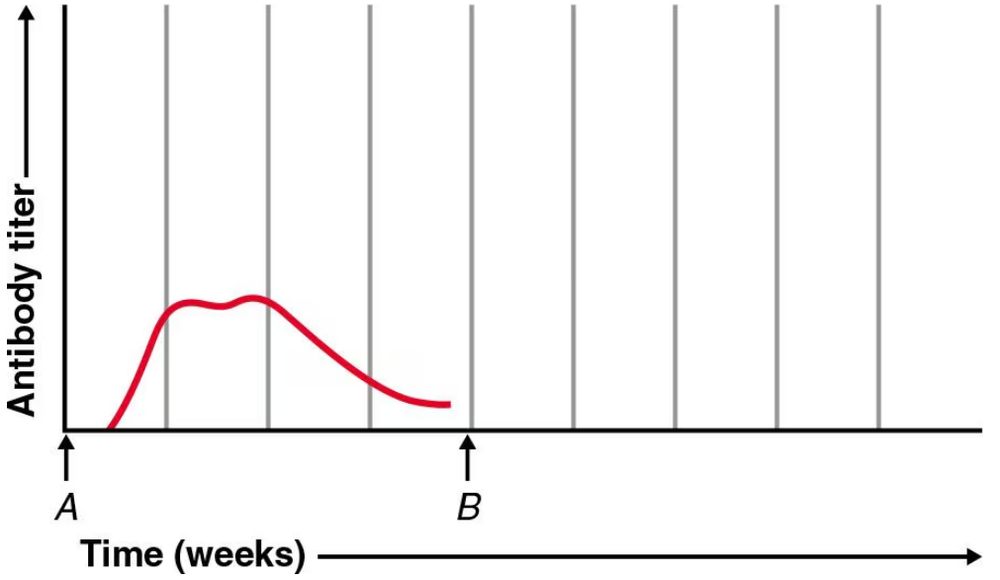
a. In the following graph, at time A the host was injected with tetanus toxoid. Show the response to a booster dose at time B.
b. Draw the antibody response of this same individual to exposure to a new antigen at time B.
Problem 6
Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
The first antibodies synthesized; especially effective against microorganisms.
Problem 7
Match the following choices to the statements in questions 5–7:
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
Antibodies that are bound to mast cells and involved in allergic reactions.
Problem 7
How would each of the following prevent infection?
a. Antibodies against Neisseria gonorrhoeae fimbriae
b. Antibodies against host cell mannose
Problem 8
Explain why a person who recovers from a disease can attend others with the disease without fear of contracting it.
Problem 8
Put the following in the correct sequence to elicit an antibody response:
(1) TH cell produces cytokines
(2) B cell contacts antigen
(3) antigen fragment goes to surface of the B cell
(4) TH recognizes antigen fragment and MHC
(5) B cell proliferates.
a. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
b. 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
c. 3, 4, 5, 1, 2
d. 2, 3, 4, 1, 5
e. 4, 5, 3, 1, 2
Problem 9
A kidney-transplant patient experienced a cytotoxic rejection of the new kidney. Place the following in order for that rejection:
(1) apoptosis occurs
(2) CD8⁺ T cell becomes CTL
(3) granzymes released
(4) MHC class I activates CD8⁺ T cell
(5) perforin released
a. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
b. 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
c. 4, 2, 5, 3, 1
d. 3, 4, 5, 1, 2
e. 2, 3, 4, 1, 5
Problem 9
How can a human make 100 billion different antibodies with only 25,000 different genes?
Problem 10
Patients with Chédiak-Higashi syndrome suffer from various types of cancer. These patients are most likely lacking which of the following?
a. Treg cells
b. TH1 cells
c. B cells
d. NK cells
e. TH2 cells
Problem 10
How can a human make 100 billion different antibodies with only 25,000 different genes?