Back
BackProblem 1
A broad-spectrum drug is best described as
a. bactericidal against a wide range of species.
b. bacteriostatic against a wide range of species.
c. effective against a wide range of species.
d. empiric therapy.
e. selectively toxic.
Problem 2
A patient who is not a healthcare worker is diagnosed with C. difficile pseudomembranous colitis. What most likely led to this infection?
a. The patient was recently treated with a bacteriostatic drug.
b. The patient was recently treated with a broad-spectrum drug.
c. The patient was treated with a bactericidal drug.
d. The patient recently became immune compromised and therefore had an increased risk for infection.
e. The patient was recently exposed to someone with an active C. difficile infection.
Problem 3
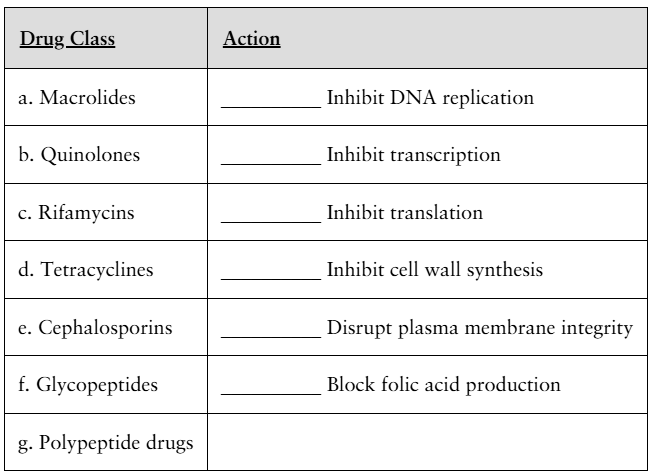
Match the antimicrobial drug class to its action. You may assign more than one drug class to a given action and some actions may not be applicable.
Problem 4
A patient has an uncomplicated infection with a Gram-negative bacterium. He also has a history of penicillin allergy. Which drug is the best treatment option for this patient?
a. Ampicillin
b. A first-generation cephalosporin
c. A carbapenem
d. Isoniazid
e. Azithromycin
Problem 5
Which drug family would be the most effective to treat a patient diagnosed with a MRSA infection?
a. Penicillins
b. Third-generation cephalosporins
c. Carbapenems
d. Lincosamides
e. Aminoglycosides
Problem 6
What advantages might a semisynthetic antimicrobial drug have over an antibiotic?
Problem 7
Choose the true statement(s) about therapeutic index (TI). Select all that apply.
a. A drug with a high therapeutic index would be effective above the dose at which it is potentially toxic.
b. A narrow TI is preferable.
c. A drug for which the maximum safe dose is close to the minimum effective dose would have a high TI.
d. It is one measure of a drug’s general safety.
e. A drug that is not selectively toxic would most likely have a high TI.
Problem 8
The difference between a synthetic drug and a semisynthetic drug is that
a. the semisynthetic drug is a modified synthetic drug.
b. the synthetic drug is a modified natural drug.
c. the synthetic drug is a modified semisynthetic drug.
d. the semisynthetic drug is a modified natural drug.
Problem 9
Which of the following antimicrobial properties would be the most crucial to consider in developing a new antimicrobial?
a. Selective toxicity
b. Ease of administration
c. Lack of drug interactions
d. Long half-life
e. The drug’s capacity to be bactericidal
Problem 10
Assume a bacterium makes beta-lactamase. Could you still use a glycopeptide drug to treat an infection caused by this bacterium? Explain your reasoning.
Problem 11
Assume a clinical sample yields a strain of S. aureus containing a plasmid that encodes two antimicrobial-resistance genes. How did the bacterium most likely acquire these new resistance genes?
a. The strain was intrinsically resistant.
b. The strain obtained the genes through horizontal gene transfer.
c. The strain acquired the genes by a random mutation.
d. The strain picked up the genes by an efflux pump.
e. The strain acquired the genes through cell division events.
Problem 12
If a gene encoding a bacterial transpeptidase enzyme undergoes mutation, which of the following antimicrobials may no longer be effective against the mutated bacterium?
a. Macrolides
b. Polypeptide drugs
c. Tetracyclines
d. Penicillins
e. Quinolones
Problem 13
Acquired antibiotic resistance can include all of the following except:
a. Altering an enzyme that a given drug may target
b. Making endospores
c. Altering a point of entry for a drug
d. Making enzymes that inactivate a drug
e. Increasing the number of efflux pumps that are active in a cell
Problem 14
Mark the following as true or false, and then correct the false statements so they are true.
a. Human cells make drug efflux pumps.
b. The minimum bactericidal concentration is the minimum concentration of the drug that kills at least 50 percent of the bacteria present.
c. The E-test can reveal if a drug is bactericidal or bacteriostatic.
d. A drug that is bactericidal at one dose may be bacteriostatic at another dose.
e. The antifolate combination therapy trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole may be used to treat protozoan infections.
Problem 15
Why is it challenging to obtain selectively toxic drugs against fungi, protozoans, and viruses?
Problem 16
Choose the false statement(s). Select all that apply.
a. Antifungal drugs may target cholesterol in fungal cell membranes.
b. Azole and polyene drugs promote cell lysis by impacting fungal cell plasma membranes.
c. Echinocandin drugs inhibit fungal cell wall synthesis.
d. Antifungal drugs may target DNA replication.
e. Antifungal drugs may target protein synthesis.
Problem 17
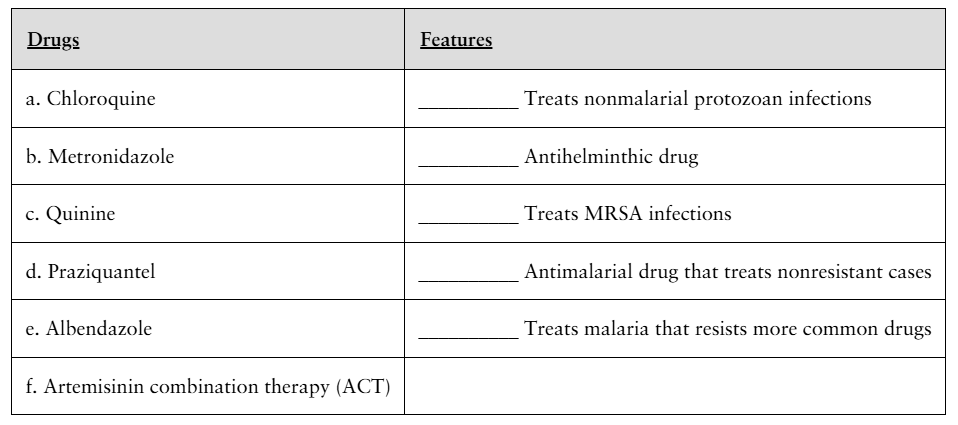
Match the antimicrobial drug to its feature. Some features may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all.
Problem 18
Which sensitivity test is best for determining the minimum bactericidal concentration and the minimum inhibitory concentration of a drug?