Back
BackProblem 1
Assume your patient has a superantigen circulating in their blood. Select the single statement that is most likely to apply to your patient.
a. They are at risk for endotoxic shock.
b. They are not up to date on their vaccinations.
c. They are infected with a Gram-positive microbe.
d. They do not have a fever.
e. They have a viral infection.
Problem 2
Which of the following is a true statement?
a. If a pathogen establishes an infection, it is described as virulent.
b. Pathogenicity is the extent of disease caused by a microbe.
c. Normal microbiota are not usually affected by host factors.
d. A pathogen’s virulence factors change over time in response to selective pressures.
e. Attenuated pathogens cause disease in a normal host.
Problem 3
Define the class of each listed exotoxin as type I, II, or III:
a. Superantigen
b. Hemolysins
c. Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins that cause food poisoning
d. AB toxin
e. Membrane-damaging toxins
f. Phospholipases
Problem 4
Which of the following is true regarding tropism?
a. It is the preference of a pathogen for a given tissue.
b. It is constant for a given microbe.
c. It limits a pathogen to infecting only one host.
d. It is determined by portal of entry.
e. It is independent of host factors.
Problem 5
Indicate the true statements and then correct the false statements so that they are true.
a. HIV is transmitted by a parenteral route.
b. Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogen that can cause disease in an immune-competent host if the normal microbiota are disrupted.
c. Gram-positive bacteria may produce endotoxin.
d. Siderophores help pathogens obtain calcium.
e. Emerging pathogens tend to exhibit expanded tropism.
f. The more toxic a substance is, the higher its LD50.
g. Virulence is the ability of a microbe to cause disease.
h. Gram-negative bacteria may produce exotoxins.
Problem 6
Select the false statement about normal microbiota.
a. They compete with pathogens.
b. They do not include potential pathogens.
c. They make vitamins for the host.
d. They train the immune system.
e. A disruption in their balance can lead to disease.
Problem 7
Pili, fimbriae, and sialic acid binding factors are examples of ________, which are virulence factors that allow pathogens to ________ host tissues––an essential early step in pathogenesis. In contrast, flagella, collagenases, and coagulases tend to act as ________, which help pathogens spread deeper into host tissues.
Problem 8
What is a reservoir, and why can C. difficile use a fomite as an effective environmental reservoir?
Problem 9
Toxigenic microbes produce _______. A high ID50 would suggest _______, and a low LD50 would suggest _______.
Problem 10
A pathogen that makes endotoxin, enters through the fecal–oral route, and lacks a nucleus is most likely a
a. Virus.
b. Gram-positive bacterium.
c. Gram-negative bacterium.
d. Protozoan pathogen.
e. There is not enough information to answer this question.
Problem 11
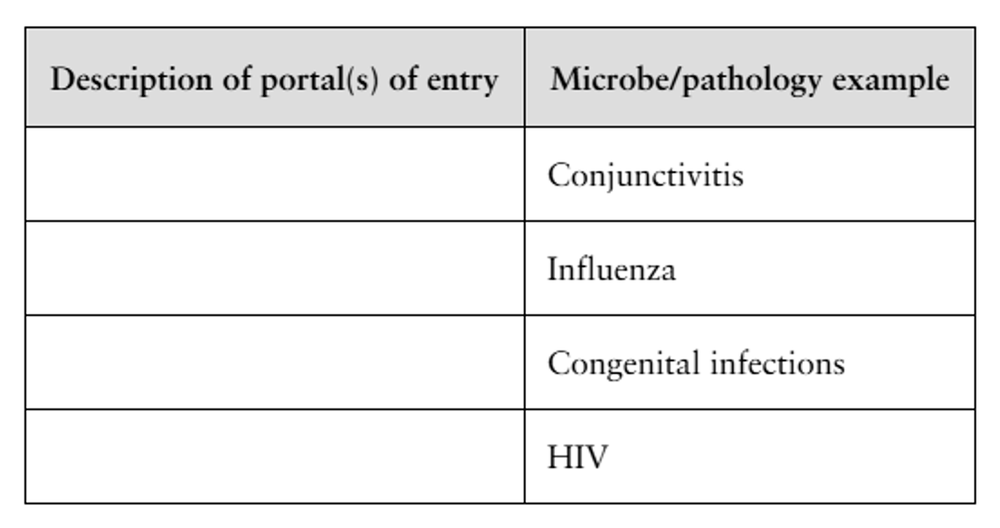
Complete the table:
Problem 12
Which of the following is false regarding biofilms?
a. They tend to consist of one species of microbe.
b. They are platforms on which pathogens may adhere.
c. They form on indwelling devices.
d. They may harbor pathogens.
e. They can form on natural and manufactured surfaces.
Problem 13
Make a Venn diagram to compare and contrast endotoxins and exotoxins.
Problem 14
What three main options can a pathogen pursue following adhesion?
Problem 15
Which of the following is false regarding toxemia?
a. It can be caused by bacteria or fungi.
b. It is localized in the patient’s body.
c. It can be caused by endotoxins.
d. It can be caused by exotoxins.
e. Some forms are vaccine preventable.
Problem 16
What precautions or actions would apply to an HIV/AIDS patient? Select all that apply.
a. Droplet precautions
b. Standard precautions
c. BSL-4 precautions
d. Universal precautions
e. AFB precautions
f. Isolation practices
Problem 18
Which of the following is/are features of endotoxic shock? Select all that apply.
a. Fever
b. Confusion
c. Hypertension
d. Bradycardia
e. Decreased respiratory rate
f. Achiness
Problem 20
Place the following steps for infection in order from first to last:
- Invade tissues and obtain nutrients
- Adhere to host tissues
- Enter the host
- Exit the host
- Evade immune defenses
Problem 21
What BSL would an airborne pathogen that causes potentially deadly, but treatable, disease be placed into? Explain your answer.