Back
BackProblem 1
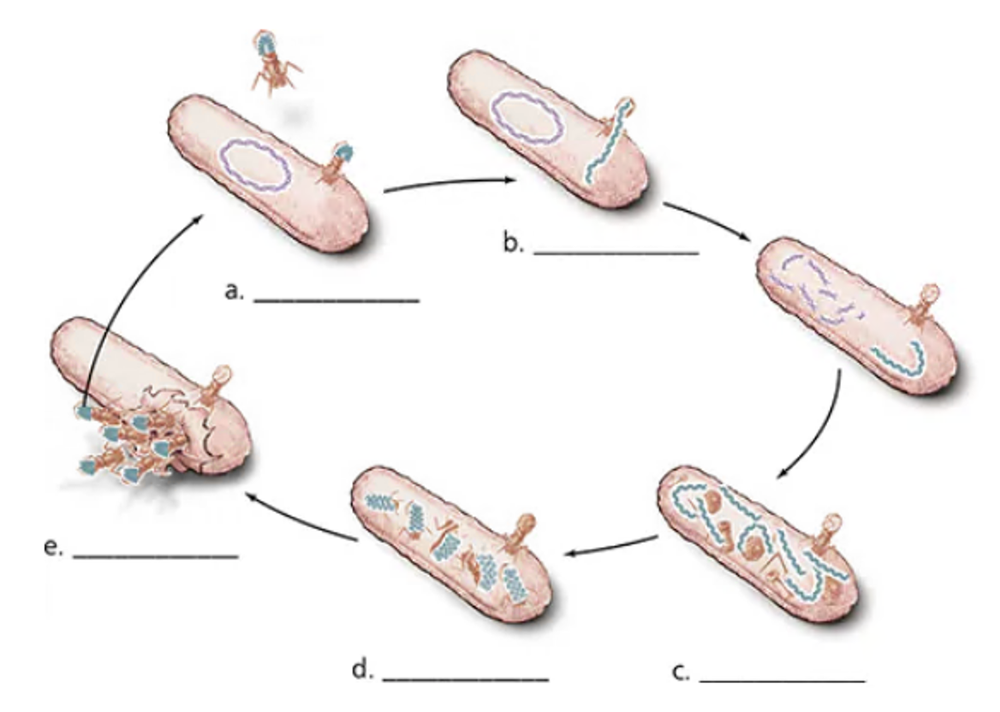
Label each step in the bacteriophage replication cycle below.
Problem 1
Which of the following is not an acellular agent?
a. Viroid
b. Virus
c. Rickettsia
d. Prion
Problem 1
Match each numbered term with its following description.
1. _________ Uncoating
2. _________ Prophage
3. _________ Retrovirus
4. _________ Bacteriophage
5. _________ Capsid
6. _________ Envelope
7. _________ Virion
8. _________ Provirus
9. _________ Benign tumor
10. ________ Cancer
A. Dormant virus in a eukaryotic cell
B. A virus that infects a bacterium
C. Transcribes DNA from RNA
D. Protein coat of virus
E. A membrane on the outside of a virus
F. Complete viral particle
G. Inactive virus within bacterial cell
H. Removal of capsomeres from a virion
I. Invasive neoplastic cells
J. Harmless neoplastic cells
Problem 1
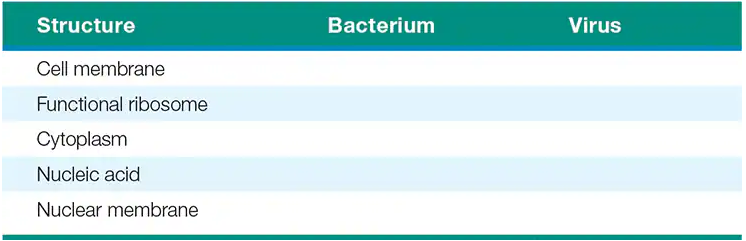
Compare and contrast a bacterium and a virus by writing either “Present” or “Absent” for each of the following structures.
Problem 2
Describe the five phases of a generalized lytic replication cycle.
Problem 2
Identify the viral capsid shapes.
a. ___________ <IMAGE>
b. ___________ <IMAGE>
c. ___________ <IMAGE>
d. ___________ <IMAGE>
Problem 2
Which of the following statements is true?
a. Viruses move toward their host cells.
b. Viruses are capable of metabolism.
c. Viruses lack a cytoplasmic membrane.
d. Viruses grow in response to their environmental conditions.
Problem 3
Why is it difficult to treat viral infections?
Problem 3
A virus that is specific for a bacterial host is called a __________ .
a. Phage
b. Prion
c. Virion
d. Viroid
Problem 4
Describe four different ways that viral nucleic acid can enter a host cell.
Problem 4
A naked virus __________ .
a. Lacks a membranous envelope
b. Has injected its DNA or RNA into a host cell
c. Is devoid of capsomeres
d. Is one that is unattached to a host cell
Problem 5
Which of the following statements is false?
a. Viruses may have circular DNA.
b. dsRNA is found in bacteria more often than in viruses.
c. Viral DNA may be linear.
d. Typically, viruses have DNA or RNA but not both.
Problem 5
Contrast lysis and budding as means of release of virions from a host cell.
Problem 6
When a eukaryotic cell is infected with an enveloped virus and sheds viruses slowly over time, this infection ___________ .
a. Is called a lytic infection
b. Is a prophage cycle
c. Is called a persistent infection
d. Is caused by a quiescent virus
Problem 6
What is the difference between a virion and a virus particle?
Problem 7
How is a provirus like a prophage? How is it different?
Problem 7
Another name for a complete virus is ___________.
a. Virion
b. Viroid
c. Prion
d. Capsid
Problem 8
Which of the following viruses can be latent?
a. HIV
b. Chicken pox virus
c. Herpesviruses
d. All of the above
Problem 8
Describe lysogeny.
Problem 9
Which of the following is not a criterion for specific family classification of viruses?
a. The type of nucleic acid
b. Envelope structure
c. Capsid type present
d. Lipid composition
Problem 9
How are viruses specific for their host’s cells?
Problem 10
A clear zone of phage infection in a bacterial lawn is __________ .
a. A prophage
b. A plaque
c. Naked
d. A zone of inhibition
Problem 10
Compare and contrast diploid cell culture and continuous cell culture.