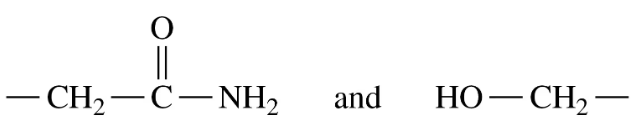Back
BackProblem 59b
Identify the amino acids and type of interaction that occurs between the following R groups in tertiary protein structures:
a.
Problem 59c
Identify the amino acids and type of interaction that occurs between the following R groups in tertiary protein structures:
c. —CH2—SH and HS—CH2—
Problem 60a
What type of interaction would you expect between the following in a tertiary structure?
a. threonine and glutamine
Problem 61a
Draw the condensed structural formula for Ser–Lys–Asp.
Problem 62b
Would you expect to find this segment at the center or at the surface of a protein? Why?
Problem 63b
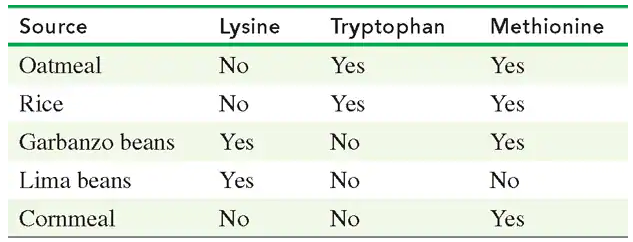
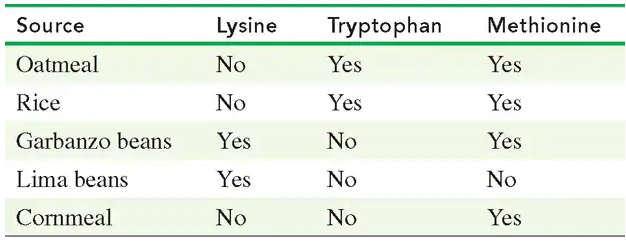
Seeds and vegetables are often deficient in one or more essential amino acids. Using the following table, state whether each combination provides all of the essential amino acids:
b. lima beans and cornmeal
Problem 64b
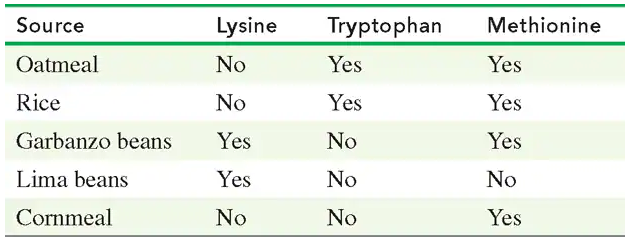
Seeds and vegetables are often deficient in one or more essential amino acids. Using the table in problem 16.63, state whether each combination provides all of the essential amino acids.
<IMAGE>
a. rice and lima beans
Problem 64c
Seeds and vegetables are often deficient in one or more essential amino acids. Using the table in problem 16.63, state whether each combination provides all of the essential amino acids.
<IMAGE>
c. oatmeal and lima beans
Problem 65c
What are some differences between each of the following pairs?
c. polar and nonpolar amino acids
Problem 65d
What are some differences between each of the following pairs?
d. dipeptides and tripeptides
Problem 66a
What are some differences between each of the following pairs?
b. an ⍺ helix and collagen
Problem 67
If glutamate were replaced by proline in a protein, how might the tertiary structure be affected?
Problem 69
How do enzymes differ from catalysts used in chemical laboratories?
Problem 70
Why do enzymes function only under mild conditions?
Problem 72b
Maltase is an enzyme that hydrolyzes maltose to two glucose molecules.
b. Draw an energy diagram for the reaction with and without maltase.
Problem 74b
Indicate whether each of the following would be a substrate (S) or an enzyme (E):
a. glucose
Problem 75b
Give the substrate of each of the following enzymes:
a. urease
Problem 76a
Give the substrate of each of the following enzymes:
a. maltase
Problem 77
How would the lock-and-key model explain that sucrase hydrolyzes sucrose, but not lactose?
Problem 80
If a blood test indicates a high level of ALT, what could be the cause?
Problem 81b
Consider the amino acids lysine, valine, and aspartate in an enzyme. State which of these amino acids have R groups that would:
b. be found in hydrophilic regions
Problem 81c
Consider the amino acids lysine, valine, and aspartate in an enzyme. State which of these amino acids have R groups that would:
c. form hydrogen bonds
Problem 81d
Consider the amino acids lysine, valine, and aspartate in an enzyme. State which of these amino acids have R groups that would:
d. form salt bridges
Problem 82d
Consider the amino acids histidine, phenylalanine, and serine in an enzyme. State which of these amino acids have R groups that would:
d. form salt bridges