Back
BackProblem 31c
What is the reactant for each of the following enzymes?
a. galactase
Problem 33c
What is the name of the class of enzymes that would catalyze each of the following reactions?
c. converting glucose (C6H12O6) to fructose (C6H12O6).
Problem 34a
What is the name of the class of enzymes that would catalyze each of the following reactions?
a. addition of water to a double bond
Problem 34c
What is the name of the class of enzymes that would catalyze each of the following reactions?
c. splitting peptide bonds in proteins
Problem 35b
Match the terms (1) enzyme–substrate complex, (2) enzyme, and (3) substrate with each of the following:
b. the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
Problem 35c
Match the terms (1) enzyme–substrate complex, (2) enzyme, and (3) substrate with each of the following:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
Problem 36a
Match the terms (1) active site, (2) lock-and-key model, and (3) induced-fit model with each of the following:
a. the portion of an enzyme where catalytic activity occurs
Problem 37a
Write an equation that represents an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
Problem 37b
How is the active site different from the whole enzyme structure?
Problem 38b
After the products have formed, what happens to the enzyme?
Problem 39
What are isoenzymes?
Problem 40
How is the LDH isoenzyme in the heart different from the LDH isoenzyme in the liver?
Problem 41
A patient arrives in an emergency department complaining of chest pains. What enzymes would you test for in the blood serum?
Problem 43a
Trypsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes polypeptides, functions in the small intestine at an optimum pH of 7.7 to 8.0. How is the rate of a trypsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
a. changing the pH to 3.0
Problem 43b
Trypsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes polypeptides, functions in the small intestine at an optimum pH of 7.7 to 8.0. How is the rate of a trypsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
b. running the reaction at 75 °C
Problem 44a
Pepsin, a peptidase that hydrolyzes proteins, functions in the stomach at an optimum pH of 1.5 to 2.0. How is the rate of a pepsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
a. changing the pH to 5.0
Problem 45
The following graph shows the activity versus pH curves for pepsin, sucrase, and trypsin. Estimate the optimum pH for each.
<IMAGE>
Problem 46a
Refer to the graph in problem 16.45 to determine if the reaction rate in each condition will be at the optimum rate or not.
<IMAGE>
a. trypsin, pH 5.0
Problem 47b
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive enzyme inhibitor:
a. The inhibitor has a structure similar to the substrate.
Problem 47d
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive enzyme inhibitor:
d. The structure of the inhibitor is not similar to the substrate.
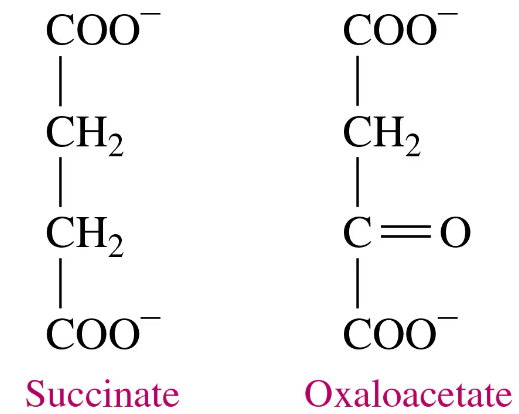
Problem 48a
Oxaloacetate is an inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase.
a. Would you expect oxaloacetate to be a competitive or a noncompetitive inhibitor? Why?
Problem 49b
Methanol and ethanol are oxidized by alcohol dehydrogenase. In methanol poisoning, ethanol is given intravenously to prevent the formation of formaldehyde that has toxic effects.
b. Would ethanol compete for the active site or bind to a different site?
Problem 50a
In humans, the antibiotic amoxicillin (a type of penicillin) is used to treat certain bacterial infections.
a. Does the antibiotic inhibit enzymes in humans?
Problem 50c
In humans, the antibiotic amoxicillin (a type of penicillin) is used to treat certain bacterial infections.
c. Is amoxicillin a reversible or irreversible inhibitor?
Problem 55a
Ethylene glycol (HO—CH2—CH2—OH) is a major component of antifreeze. If ingested, it is first converted to HOOC—CHO (oxoethanoic acid) and then to HOOC—COOH (oxalic acid), which is toxic.
<IMAGE>
a. What class of enzyme catalyzes the reactions described?
Problem 55b
Ethylene glycol (HO—CH2—CH2—OH) is a major component of antifreeze. If ingested, it is first converted to HOOC—CHO (oxoethanoic acid) and then to HOOC—COOH (oxalic acid), which is toxic.
<IMAGE>
b. The treatment for the ingestion of ethylene glycol is an intravenous solution of ethanol. How might this help prevent toxic levels of oxalic acid in the body?
Problem 56a
Adults who are lactose intolerant cannot break down the disaccharide in milk products. To help digest dairy food, a product known as Lactaid can be given prior to consuming dairy products. (16.4, 16.5)
a. What is the name of enzyme present in Lactaid, and what is the major class of this enzyme?
Problem 56b
Adults who are lactose intolerant cannot break down the disaccharide in milk products. To help digest dairy food, a product known as Lactaid can be given prior to consuming dairy products. (16.4, 16.5)
b. What might happen to the enzyme if the Lactaid were stored at 55 °C?
Problem 58a
Fresh pineapple contains the enzyme bromelain that hydrolyzes peptide bonds in proteins.
<IMAGE>
a. The directions for a gelatin (protein) dessert say not to add fresh pineapple. However, canned pineapple where pineapple is heated to high temperatures can be added. Why?
Problem 58b
Fresh pineapple contains the enzyme bromelain that hydrolyzes peptide bonds in proteins.
<IMAGE>
b. Fresh pineapple is used in a marinade to tenderize tough meat. Why?