Draw the condensed structural formulas for the products of the reaction of aspartate and α-ketoglutarate which is catalyzed by aspartate transaminase (AST).
Ch.18 Metabolic Pathways and ATP Production

Timberlake13th EditionChemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryISBN: 9780134421353Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 18, Problem 75d
Identify the type of food as carbohydrate, fat, or protein that gives each of the following digestion products:
d. glycerol
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the digestion process: During digestion, macromolecules such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are broken down into smaller molecules. Each type of macromolecule produces specific digestion products.
Recall the digestion products of fats: Fats (lipids) are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids by enzymes such as lipase. This is a key characteristic of fat digestion.
Identify glycerol: Glycerol is a three-carbon molecule that is part of the structure of triglycerides, which are the main form of fat in the diet. Its presence indicates fat digestion.
Connect glycerol to fats: Since glycerol is a product of fat digestion, the type of food that produces glycerol during digestion is fat.
Conclude the answer: Based on the digestion process and the specific product glycerol, the type of food associated with glycerol is fat.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Glycerol
Glycerol is a simple polyol compound that serves as a backbone for triglycerides, which are the main form of fat storage in the body. It is produced during the digestion of fats, specifically when triglycerides are broken down by enzymes. Understanding glycerol's role is essential for recognizing how fats are metabolized and utilized for energy.
Recommended video:
Guided course
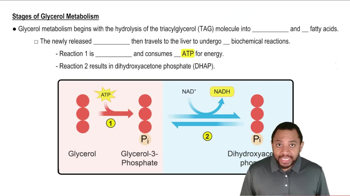
Glycerol Metabolism Concept 2
Digestion of Fats
The digestion of fats involves the breakdown of triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids through the action of lipases. This process occurs primarily in the small intestine, where bile salts emulsify fats, making them more accessible to digestive enzymes. Recognizing this process is crucial for understanding how dietary fats contribute to energy production and overall metabolism.
Recommended video:
Guided course
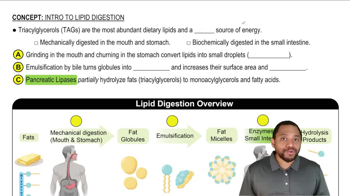
Intro to Lipid Digestion Concept 1
Macronutrients
Macronutrients are the nutrients required in large amounts for energy and bodily functions, including carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Each macronutrient has distinct roles in the body; for instance, fats provide concentrated energy and are essential for hormone production. Understanding the classification of macronutrients helps in identifying the digestion products associated with each type.
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Arachidic acid is a C20 fatty acid found in peanut and fish oils.
a. How many cycles of β oxidation are needed for the complete oxidation of arachidic acid?
Textbook Question
Arachidic acid is a C20 fatty acid found in peanut and fish oils.
c. Calculate the total ATP yield from the complete β oxidation of arachidic acid by completing the following:
Textbook Question
Identify the type of food as carbohydrate, fat, or protein that gives each of the following digestion products:
e. amino acids
Textbook Question
Identify each of the following as a six-carbon or a three-carbon compound and arrange them in the order in which they occur in glycolysis:
a. 3-phosphoglycerate
Textbook Question
When is pyruvate converted to lactate in the body?
