A specific virus contains RNA as its genetic material.
a. Why would reverse transcription be used in the life cycle of this type of virus?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
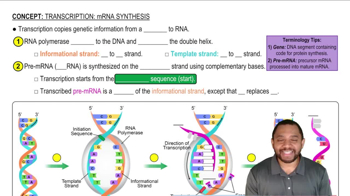
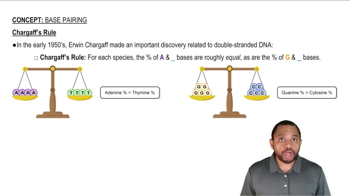

A specific virus contains RNA as its genetic material.
a. Why would reverse transcription be used in the life cycle of this type of virus?
A specific virus contains RNA as its genetic material.
b. What is the name of this type of virus?
How do protease inhibitors disrupt the life cycle of the HIV virus?
The following is a segment of the template strand of human BRCA1 gene:
TGG AAT TAT CTG CTC TTC GCG
b. Write the three-letter and one-letter abbreviations for the corresponding peptide segment.
The following is a segment of the template strand of human BRCA1 gene:
TGG AAT TAT CTG CTC TTC GCG
c. If there is a point mutation in the fourth nucleotide triplet and A replaces G, what is the change, if any, in the amino acid sequence?
Answer the following questions for the given section of DNA:
a. Complete the bases in the parent and new strands.