Identify the type of transport described by each of the following:
a. An ion moves from low to high concentration in the cell.

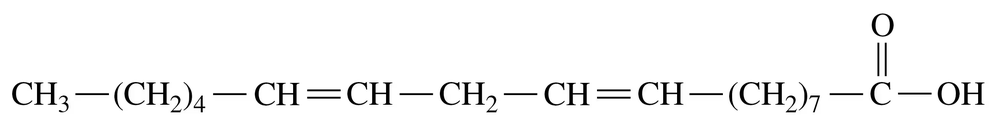
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Identify the type of transport described by each of the following:
a. An ion moves from low to high concentration in the cell.
Palm oil has a high level of glyceryl tripalmitate (tripalmitin). Draw the condensed structural formula for glyceryl tripalmitate.
<IMAGE>
Identify each of the following as a saturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, omega-3, or omega-6 fatty acid:
a.
The total kilocalories and grams of fat for some typical meals at fast-food restaurants are listed here. Calculate the number of kilocalories and the percentage of total kilocalories from fat (1 gram of fat = 9 kcal). Round answers to the tens place.
a. a beef burrito, 470 kcal, 21 g of fat
Identify each of the following as a fatty acid, soap, triacylglycerol, wax, glycerophospholipid, sphingolipid, or steroid:
a. beeswax