Textbook Question
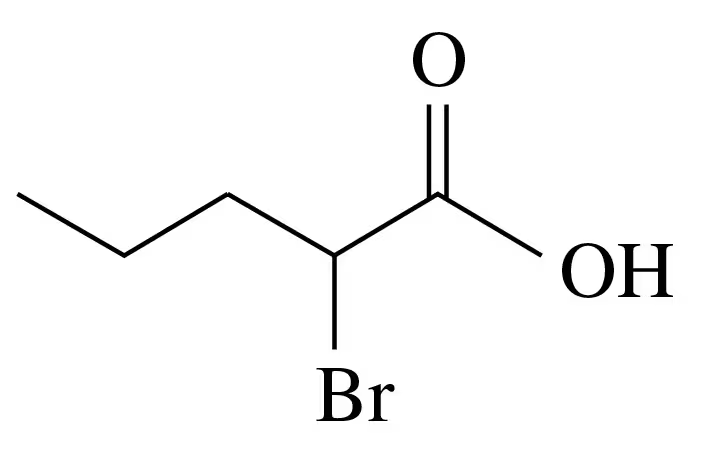
Write the IUPAC and common name, if any, for each of the following carboxylic acids:
b.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Write the IUPAC and common name, if any, for each of the following carboxylic acids:
b.
Draw the condensed structural formulas for a and b and line-angle formulas for c and d:
a. 3,4-dibromobutanoic acid
Draw the condensed structural formulas for a and b and line-angle formulas for c and d:
c. 3-ethylbenzoic acid
Identify the compound in each group that is most soluble in water. Explain.
b. pentane, 1-hexanol, propanoic acid