Draw the condensed structural formulas and give the IUPAC names for all the aldehydes and ketones that have the formula C5H10O. (12.3)

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
Ch.12 Alcohols, Thiols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones Problem 66a
Problem 66aA compound with the formula C5H10O oxidizes to give 3-pentanone. Draw the condensed structural formula and give the IUPAC name for the compound.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
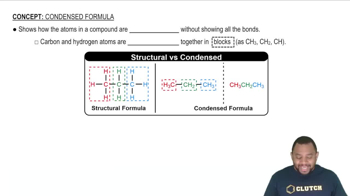
Condensed Structural Formula
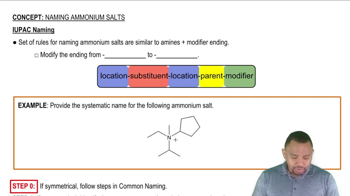
IUPAC Nomenclature
Oxidation in Organic Chemistry
A compound with the formula C4H8O is synthesized from 2-methyl-1-propanol and oxidizes easily to give a carboxylic acid. Draw the condensed structural formula and give the IUPAC name for the compound.
Compound A is a primary alcohol whose formula is C3H8O. When compound A is heated with strong acid, it dehydrates to form compound B (C3H6). When compound A is oxidized, compound C (C3H6O) forms. Draw the condensed structural formulas and give the IUPAC names for compounds A, B, and C.
Compound X is a secondary alcohol whose formula is C3H8O. When compound X is heated with strong acid, it dehydrates to form compound Y (C3H6). When compound X is oxidized, compound Z (C3H6O) forms, which cannot be oxidized further. Draw the condensed structural formulas and give the IUPAC names for compounds X, Y, and Z.