Textbook Question
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alkanes and cycloalkanes:
a. <IMAGE>

 Timberlake 13th Edition
Timberlake 13th Edition Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
Ch.11 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Problem 11a
Problem 11a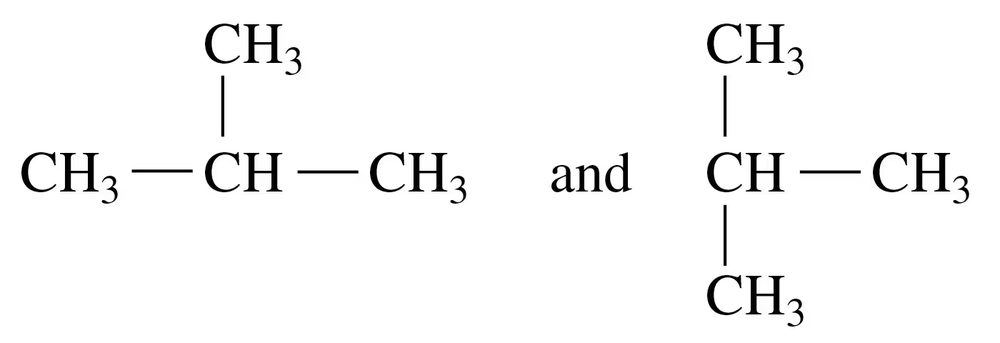
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alkanes and cycloalkanes:
a. <IMAGE>
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following alkanes and cycloalkanes:
c.
Draw the condensed structural formula for alkanes or the line-angle formula for cycloalkanes for each of the following:
c. heptane
Indicate whether each of the following pairs represent structural isomers or the same molecule:
b.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
b.
Give the IUPAC name for each of the following:
c.