Back
BackProblem 30a
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
a. Cholesterol is attached to this protein in order to move through the blood system.
Problem 30b
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
b. Ionized zinc is attached to this protein so the protein can function.
Problem 30c
For each of the conjugated proteins described, identify to which class of conjugated protein it belongs.
c. Phosphate groups are attached to this protein.
Problem 31
Both α-keratin and tropocollagen have helical secondary structure. How do these molecules differ in (a) amino acid composition and (b) three-dimensional structure?
Problem 32
Another endoprotease is trypsin. Trypsin hydrolyzes peptide bonds on the carboxyl side of lysine and arginine. If the following peptide sequence is hydrolyzed by trypsin, how many fragments will there be? Use the three-letter amino acid abbreviations to write the fragments out.
Ala-Phe-Lys-Cys-Gly-Asp-Arg-Leu-Leu-Phe-Gly-Ala
Problem 33
If the same peptide found in Problem 18.32 is subjected to acid hydrolysis, how many fragments will result? Why?
Ala-Phe-Lys-Cys-Gly-Asp-Arg-Leu-Leu-Phe-Gly-Ala
Problem 34a
Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
a. Val
Problem 34d
Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
d. Glu-Asp
Problem 34e
Draw the structure of the following amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides at low pH (pH 1) and high pH (pH 14). At each pH, assume that all functional groups that might do so are ionized.
e. Gln-Ala-Asn
Problem 35a
Interactions of amino acids on the interior of proteins are key to the shapes of proteins. In group (a), which pairs of amino acids form hydrophobic interactions? In group (b), which pairs form ionic interactions? Which pairs in group (c) form hydrogen bonds?
a. 1 Pro . . . Phe
2 Lys . . . Ser
3 Thr . . . Leu
4 Ala . . . Gly
Problem 36
Draw the hexapeptide Asp-Gly-Phe-Leu-Glu-Ala in linear form showing all of the atoms, and show (using dotted lines) the hydrogen bonding that stabilizes this structure if it is part of an α-helix.
Problem 37
Compare and contrast the characteristics of fibrous and globular proteins. Consider biological function, water solubility, amino acid composition, secondary structure, and tertiary structure. Give examples of three fibrous and three globular proteins. (Hint: Make a table.)
Problem 38a
Cell membranes are studded with proteins. Some of these proteins, involved in the transport of molecules across the membrane into the cell, span the entire membrane and are called transmembrane proteins. The interior of the cell membrane is hydrophobic and nonpolar, whereas both the extracellular and intracellular fluids are water-based.
a. List three amino acids you would expect to find in the part of a transmembrane protein that lies within the cell membrane.
Problem 39
Threonine has two chiral centers. Draw L-threonine and indicate which carbon atoms are chiral. Which carbon atom is responsible for D and L configuration?
Problem 40
Name four biological functions of proteins in the human body, and give an example of a protein for each function.
Problem 41a
What kind of biological function would each of the following proteins perform?
a. Human growth hormone
Problem 41c
What kind of biological function would each of the following proteins perform?
c. Protease
Problem 42a
What amino acids do the following abbreviations stand for? Draw the structure of each.
a. Val
Problem 44a
Name and draw the structures of the amino acids that fit the following descriptions:
a. Contains a thiol group
Problem 45a
Name and draw the structures of the amino acids that fit the following descriptions:
a. Contains an isopropyl group
Problem 48
Draw leucine and identify any chiral carbon atoms with arrows.
Problem 50
Is phenylalanine hydrophilic or hydrophobic? Explain why.
Problem 52
At neutral pH, which of the following amino acids has a net positive charge, which has a net negative charge, and which is neutral? (Hint: Draw the various charged forms of each amino acid before deciding.)
a. Asparagine
b. Lysine
c. Proline
Problem 54
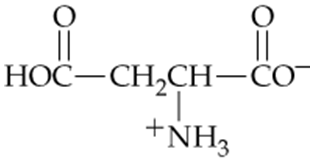
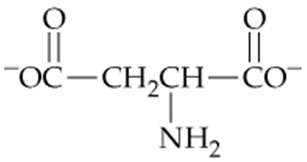
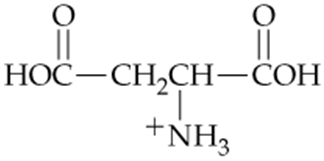
Which of the following forms of aspartic acid would you expect to predominate at low pH, neutral pH, and high pH?
a.
b.
c.
Problem 55
Which form of aspartic acid in Problem 18.54 is the zwitterion? What is the pI for the zwitterion?
a.
b.
c.
Problem 58
Proteins are usually least soluble in water at their isoelectric points. Explain.
Problem 59
How could you make the zwitterion of aspartic acid more soluble in water?
Problem 60
Use the three-letter abbreviations to name all tripeptides that contain valine, methionine, and leucine.
Problem 61
Write structural formulas for the two dipeptides that contain leucine and aspartate.
Problem 62
The endorphins are a group of naturally occurring neurotransmitters that act in a manner similar to morphine to control pain. Research has shown that the biologically active parts of the endorphin molecules are simple pentapeptides called enkephalins. Draw the structure of the methionine enkephalin with the sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met. Identify the N-terminal and C-terminal amino acids.