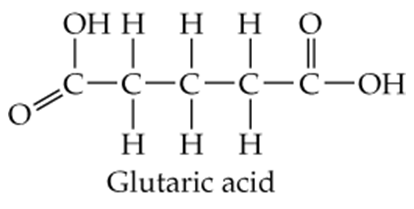
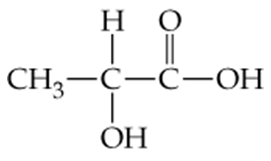
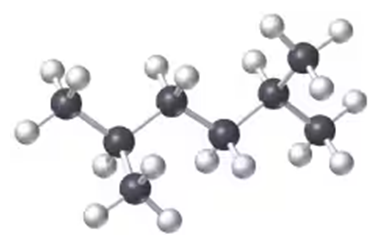
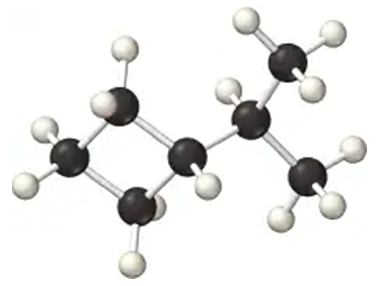
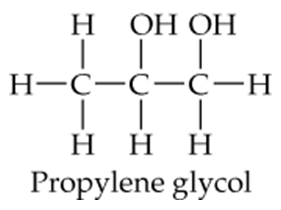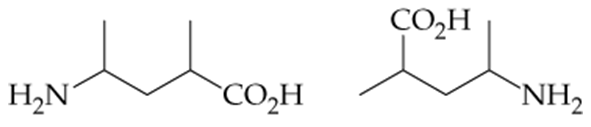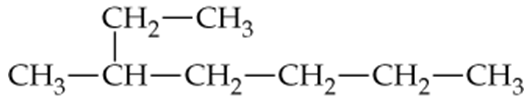Back
BackProblem 2a
Draw structures for molecules that fit the following descriptions:
(a) C3H6O containing an aldehyde functional group
Problem 2c
Draw structures for molecules that fit the following descriptions:
(c) C3H6O2 containing a carboxylic acid functional group
Problem 3b
Draw the straight-chain isomer with the formula (b) C9H20.
Problem 4
There are two branched-chain isomers with the formula C7H16, where the longest chain in the molecule is six carbons long. Draw them.
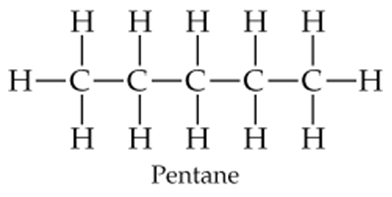
Problem 5a
Draw the following three isomers of C5H12 as condensed structures:
a.
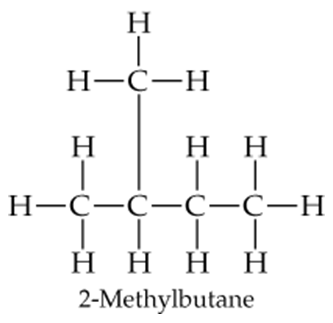
Problem 5b
Draw the following three isomers of C5H12 as condensed structures:
b.
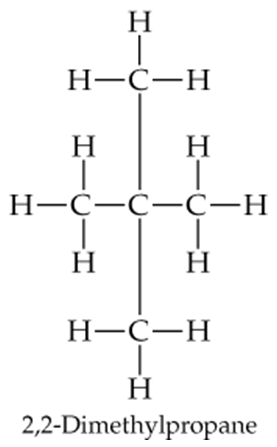
Problem 5c
Draw the following three isomers of C5H12 as condensed structures:
c.
Problem 7a
Convert the following line structures to condensed structures:
a.
Problem 7b
Convert the following line structures to condensed structures:
b.
Problem 8
Draw both condensed and line structures for the chemicals listed in Problem 12.1.
a.
b.
c.
d.
Problem 10a
Are the pairs of compounds shown below the same molecule, isomers, or different molecules?
a.
Problem 12a
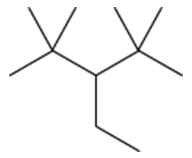
What are the IUPAC names of the following alkanes?
a.
Problem 13c
Draw both condensed and line structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names and label each carbon as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary.
c. 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
Problem 14a
Draw and name alkanes that meet the following descriptions:
a. A 5-carbon alkane with a tertiary carbon atom
Problem 17
Write the structures of all singly chlorinated products that form when 2,4-dimethylpentane is reacted with Cl2.
Problem 18b
What are the IUPAC names of the following cycloalkanes? Remember to assign priority to the attached groups alphabetically.
b.
Problem 20c
What is wrong with the following names? It will be helpful to draw the structures as named before making your decision.
c. 1-Ethyl-2-methyl-3-ethylcyclopentane
Problem 22a
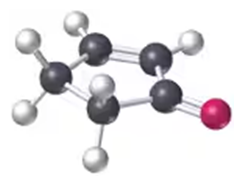
Convert the following models into line drawings (back = C; white = H; blue = N):
a.
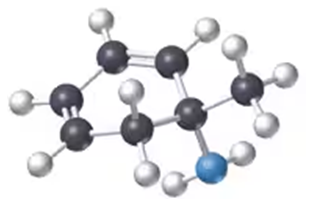
Problem 22b
Convert the following models into line drawings (back = C; white = H; blue = N):
b.
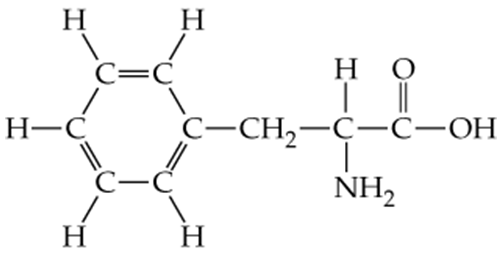
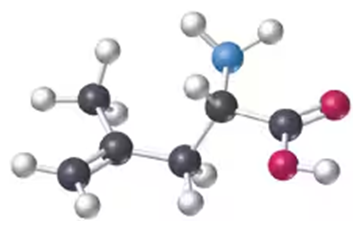
Problem 23b
Convert the following models into line drawings and identify the functional groups in each:
b.
Problem 24a
Give the IUPAC names for the following alkanes:
a.
Problem 24b
Give the IUPAC names for the following alkanes:
b.
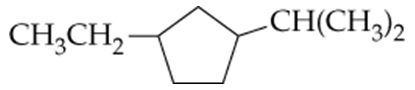
Problem 25b
Give the IUPAC names for the following cycloalkanes:
b.
Problem 27
What characteristics of carbon make possible the existence of so many different organic compounds?
Problem 29
Why are most organic compounds nonconducting and insoluble in water?
Problem 31a
For each of the following, give an example of a member compound containing 5 carbons total:
(a) Alcohol
Problem 31d
For each of the following, give an example of a member compound containing 5 carbons total:
(d) Ether