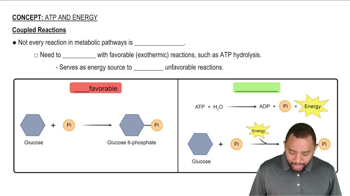
Which of the following reactions in glycolysis produce ATP or NADH?
a. glucose to glucose-6-phosphate

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Which of the following reactions in glycolysis produce ATP or NADH?
a. glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
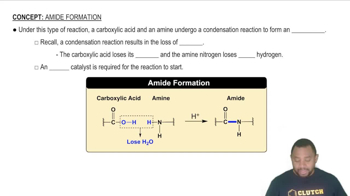
Which of the reactions given in Problems 12.72 represent isomerizations where the reactants and products are structural isomers?
a. glucose to glucose-6-phosphate
b. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
c. dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
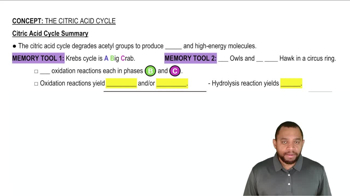
Refer to the diagram of the citric acid cycle in Figure 12.11 to answer each of the following:
d. Name the reactions where secondary alcohols are oxidized to ketones.
If there are no reactions in the citric acid cycle that use oxygen, O2, why does the cycle operate only in aerobic conditions?
Identify the following as the reduced or oxidized form:
a. NAD+
Identify the following as the reduced or oxidized form:
c. QH2