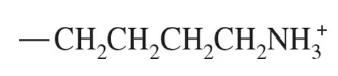Back
BackProblem 71d
Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
d. intermolecular forces between R groups
Problem 72b
Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
b. disulfide bridge
Problem 72d
Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
d. salt bridges between polypeptides
Problem 73a
For each of the following proteins, note whether the main secondary structure feature is α helix, β-pleated sheet, or both.
a. collagen
Problem 73c
For each of the following proteins, note whether the main secondary structure feature is α helix, β-pleated sheet, or both.
c. hemoglobin
Problem 73d
For each of the following proteins, note whether the main secondary structure feature is α helix, β-pleated sheet, or both.
e. hexokinase
Problem 75a
Indicate what type(s) of intermolecular forces are disrupted and what level of protein structure is changed by the following denaturing treatments:
a. an egg placed in water at 100 °C and boiled for 10 minutes
Problem 75c
Indicate what type(s) of intermolecular forces are disrupted and what level of protein structure is changed by the following denaturing treatments:
c. egg whites whipped in a mixing bowl to make meringue
Problem 76
Describe the changes that occur in the primary structure when a protein is denatured versus when a protein is hydrolyzed.
Problem 79a
Collagen contains an amino acid that is a modified form of the naturally occurring amino acid.
a. Name the natural amino acid.
Problem 84(1)
Match the terms (1) ES with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
Problem 84(2)
Match the terms (2) enzyme with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
Problem 84(3)
Match the terms (3) substrate with the following descriptions:
a. has a tertiary structure that recognizes the substrate
b. is the combination of an enzyme with the substrate
c. has a structure that fits the active site of an enzyme
Problem 85
Match the terms (1) active site, (2) lock-and-key model, and (3) induced-fit model with the following descriptions:
a. the portion of an enzyme where catalytic activity occurs
b. the active site adapts to the shape of a substrate
c. the active site has a rigid shape
Problem 86
Do the amino acids that are in the active site of an enzyme have to be near each other in the enzyme’s primary structure? If no, explain.
Problem 87
The enzyme trypsin catalyzes the breakdown of many structurally diverse proteins in foods. Does the induced-fit or lock-and-key model explain the action of trypsin better? Explain.
Problem 88
The enzyme sucrase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the disaccharide sucrose but not the disaccharide lactose. Does the induced-fit or lock-and-key model explain the action of sucrase better? Explain.
Problem 90
What type of interactions between an enzyme and its substrate help to stabilize ES?
Problem 91b
Does each of the following statements describe a simple enzyme (no cofactor or coenzyme necessary), an enzyme that requires a cofactor, or an enzyme that requires a coenzyme?
b. consists of one polypeptide chain in its active form
Problem 91c
Does each of the following statements describe a simple enzyme (no cofactor or coenzyme necessary), an enzyme that requires a cofactor, or an enzyme that requires a coenzyme?
c. contains vitamin B6 in its active site
Problem 92b
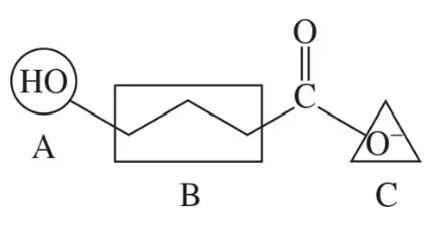
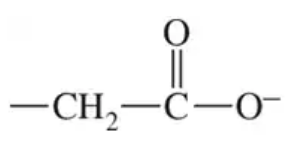
A substrate is held in the active site of an enzyme by attractive forces between the substrate and the amino acid side chains. For the outlined regions A, B, and C on the following substrate molecule:
b. Could the amino acids serine, lysine, or glutamate be present in the active site? Support your answer.
Problem 93a
If each of the following amino acid side chains is present in the active site of an enzyme, indicate whether it would (a) serve a catalytic function, (b) serve to hold the substrate, or (c) both.
a. aspartate
Problem 93d
If each of the following amino acid side chains is present in the active site of an enzyme, indicate whether it would (a) serve a catalytic function, (b) serve to hold the substrate, or (c) both.
d. lysine
Problem 95a
Pepsin, an enzyme that hydrolyzes peptide bonds in proteins, functions in the stomach at a pH optimum of 1.5 to 2.0. How is the rate of a pepsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
a. increasing the concentration of proteins
Problem 95c
Pepsin, an enzyme that hydrolyzes peptide bonds in proteins, functions in the stomach at a pH optimum of 1.5 to 2.0. How is the rate of a pepsin-catalyzed reaction affected by each of the following conditions?
c. running the reaction at 0 °C
Problem 96
Problems 10.94 and 10.95 both mention enzymes that hydrolyze peptide bonds. How do you account for the fact that pepsin has a high catalytic activity at pH 1.5 but chymotrypsin has very little activity at pH 1.5?
Problem 99
How does an irreversible inhibitor function differently than a reversible inhibitor?
Problem 104
Meats spoil due to the action of enzymes that degrade the proteins. Fresh meats can be preserved for long periods of time by freezing them. Explain how freezing meats works to prevent spoilage.
Problem 110b
Insulin is a protein hormone that functions as two polypeptide chains whose amino acid sequences are as follows:
A chain: GIVEQCCTSICSLTQLENYCN
B chain: FVNQHLCGDHLVEALYLV CGERGFFYTPKT
b. Considering the amino acid sequences, suggest how these two polypeptide chains might be held together in an active insulin molecule.