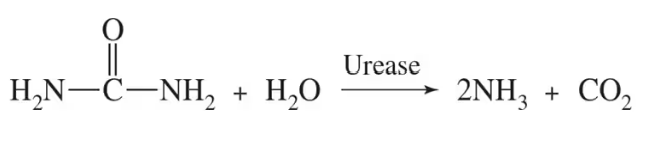Back
BackProblem 27d
What type of interaction would you expect between the side chains of each of the following pairs of amino acids in the tertiary structure of a protein?
d. glutamine and arginine
Problem 28b
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
b. Peptide bonds join amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Problem 28d
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
d. Hydrogen bonding between amino acids in the same polypeptide gives a coiled shape to the protein.
Problem 29b
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
b. Hydrogen bonds form between adjacent segments of the backbone of the same protein to form a “folded-fan” structure.
Problem 29d
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
d. Amino acids react in a condensation reaction to form a peptide bond.
Problem 30a
Myoglobin is a protein containing 153 amino acids. Approximately half of the amino acids in myoglobin have polar side chains.
a. Where would you expect these amino acid side chains to be located in the tertiary structure of the protein?
Problem 30b
Myoglobin is a protein containing 153 amino acids. Approximately half of the amino acids in myoglobin have polar side chains.
b. Where would you expect the nonpolar side chains to be?
Problem 33a
List the type of attractive force disrupted and the level of protein structure changed by the following denaturing treatments:
a. adding salt to soy milk to make tofu
Problem 35a
Identify each of the following statements as characteristic of protein denaturation or protein hydrolysis.
a. Milk curdles when lemon juice is added to it.
Problem 35b
Identify each of the following statements as characteristic of protein denaturation or protein hydrolysis.
b. A protein breaks up into amino acid fragments.
Problem 37
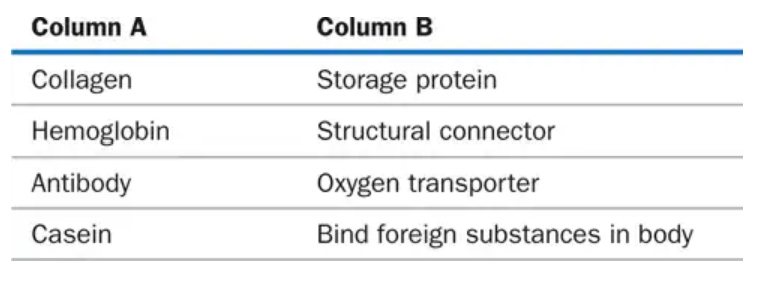
Match each protein in column A with its function in column B:
Problem 42
What is the name given to the reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction?
Problem 44
What is the name given to a small, organic nonprotein part of an enzyme that is involved in catalysis?
Problem 49
What level of protein structure is involved in the formation of an enzyme’s active site?
Problem 50
What kind of interaction attracts the cofactor Mg2+ and ATP to each other? (Hint: Look at the structure of the phosphate group.)
Problem 51a
How would the following changes affect enzyme activity for an enzyme whose optimal conditions are normal body temperature and physiological pH?
a. raising the temperature from 37 °C to 60 °C
Problem 53a
The enzyme urease functions in the body to catalyze the formation of ammonia and carbon dioxide from urea as shown:
Describe what effect the following changes would have on the rate of this reaction assuming a steady state has been reached:
a. adding excess urea
Problem 54a
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive inhibitor.
a. The structure of the inhibitor is similar to that of the substrate.
Problem 54c
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive inhibitor.
c. The inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active site.
Problem 54e
Indicate whether each of the following describes a competitive or a noncompetitive inhibitor.
e. Adding more substrate to the reaction restores the enzyme activity.
Problem 56a
Give the name and three-letter abbreviation for the amino acid described by each of the following:
a. the nonpolar amino acid with a sulfur atom in its side chain
Problem 57a
Give the name and three-letter abbreviation for the amino acid described by each of the following:
a. the polar amino acid with a benzene ring in its side chain
Problem 57c
Give the name and three-letter abbreviation for the amino acid described by each of the following:
c. the polar amino acid with a sulfur atom in its side chain
Problem 60d
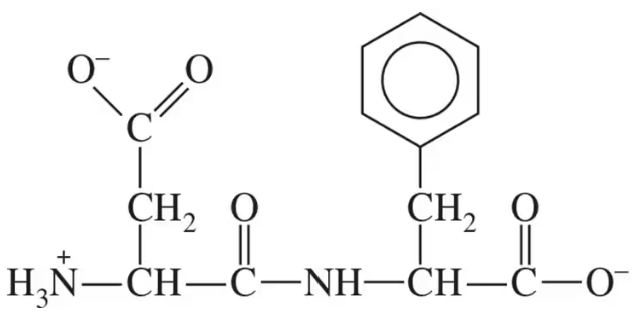
Aspartame, which is commonly known as NutraSweet™, contains the following dipeptide:
d. Draw the structure of the isomer of this dipeptide where the C-terminal and N-terminal amino acids are switched.
Problem 64
Draw the structure of the possible dipeptides formed from one alanine combining with one cysteine.
Problem 65b
Consider the amino acids glycine, proline, and lysine.
b. Using three-letter abbreviations for the amino acids, give the sequence for each of the possible tripeptides.
Problem 67b
Would you expect to find this segment at the center or on the surface of a globular protein? Why?
Problem 68
Name the covalent bond that helps to stabilize the tertiary structure of a protein.
Problem 69b
Identify some differences between the following pairs:
b. complete and incomplete proteins
Problem 71b
Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
b. hydrogen bonding between backbone atoms