Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
d. salt bridges between polypeptides

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

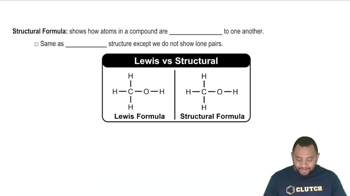

Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
d. salt bridges between polypeptides
For each of the following proteins, note whether the main secondary structure feature is α helix, β-pleated sheet, or both.
a. collagen
For each of the following proteins, note whether the main secondary structure feature is α helix, β-pleated sheet, or both.
c. hemoglobin
Indicate what type(s) of intermolecular forces are disrupted and what level of protein structure is changed by the following denaturing treatments:
a. an egg placed in water at 100 °C and boiled for 10 minutes
Indicate what type(s) of intermolecular forces are disrupted and what level of protein structure is changed by the following denaturing treatments:
c. egg whites whipped in a mixing bowl to make meringue
Describe the changes that occur in the primary structure when a protein is denatured versus when a protein is hydrolyzed.