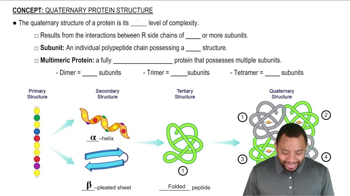
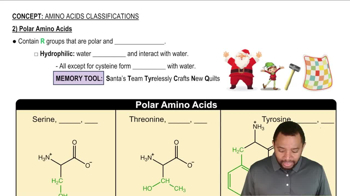
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
b. Hydrogen bonds form between adjacent segments of the backbone of the same protein to form a “folded-fan” structure.