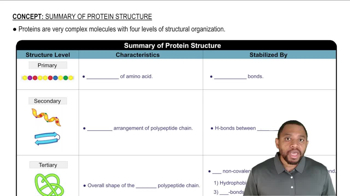
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
b. Peptide bonds join amino acids in a polypeptide chain.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
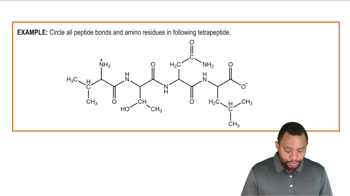
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
b. Peptide bonds join amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
d. Hydrogen bonding between amino acids in the same polypeptide gives a coiled shape to the protein.
Determine whether each of the following statements describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary structure of a protein.
b. Hydrogen bonds form between adjacent segments of the backbone of the same protein to form a “folded-fan” structure.
Myoglobin is a protein containing 153 amino acids. Approximately half of the amino acids in myoglobin have polar side chains.
a. Where would you expect these amino acid side chains to be located in the tertiary structure of the protein?
Myoglobin is a protein containing 153 amino acids. Approximately half of the amino acids in myoglobin have polar side chains.
b. Where would you expect the nonpolar side chains to be?
List the type of attractive force disrupted and the level of protein structure changed by the following denaturing treatments:
a. adding salt to soy milk to make tofu