Back
BackProblem 15
Diagram a replication fork in bacterial DNA and label the following structures or molecules.
a. DNA pol III
b. Helicase
c. RNA primer
d. Origin of replication
e. leading strand (label its polarity)
f. DNA pol I
g. Topoisomerase
h. SSB protein
i. Lagging strand (label its polarity)
j. Primase
k. Okazaki fragment
Problem 16a
Which of the following equations are true for the percentages of nucleotides in double-stranded DNA?
(A + G)/(C + T)= 1.0
Problem 16b
Which of the following equations are true for the percentages of nucleotides in double-stranded DNA?
(A + T)/(G + C)= 1.0
Problem 16c
Which of the following equations are true for the percentages of nucleotides in double-stranded DNA?
(A)/(T) = (G)/(C)
Problem 16d
Which of the following equations are true for the percentages of nucleotides in double-stranded DNA?
(A)/(C) = (G)/(T)
Problem 16e
Which of the following equations are true for the percentages of nucleotides in double-stranded DNA?
(A)/(G) = (T)(C)
Problem 17a
Which of the following equalities is not true for double-stranded DNA?
(G + T) = (A + C)
Problem 17b
Which of the following equalities is not true for double-stranded DNA?
(G + C) = (A + T)
Problem 17c
Which of the following equalities is not true for double-stranded DNA?
(G + A) = (C + T)
Problem 18
List the order in which the following proteins and enzymes are active in E. coli DNA replication: DNA pol I, SSB, ligase, helicase, DNA pol III, and primase.
Problem 19
Two viral genomes are sequenced, and the following percentages of nucleotides are identified:
Genome 1: A = 28%, C = 22%, G = 28%, T = 22%
Genome 2: A = 22%, C = 28%, G = 28%, T = 22%
Are the DNA molecules in each genome single-stranded or double-stranded?
Problem 20
Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl demonstrated that DNA replication is semiconservative in bacteria. Briefly outline their experiment and its results for two DNA replication cycles, and identify how the alternative models of DNA replication were excluded by the data.
Problem 21
Raymond Rodriguez and colleagues demonstrated conclusively that DNA replication in E. coli is bidirectional. Explain why locating the origin of replication on one side of the circular chromosomes and the terminus of replication on the opposite side of the chromosome supported this conclusion.
Problem 22
Joel Huberman and Arthur Riggs used pulse–chase labeling to examine the replication of DNA in mammalian cells. Briefly describe the Huberman–Riggs experiment, and identify how the results exclude a unidirectional model of DNA replication.
Problem 23
Why do the genomes of eukaryotes, such as Drosophila, need to have multiple origins of replication, whereas bacterial genomes, such as that of E. coli, have only a single origin?
Problem 24
Bloom syndrome (OMIM 210900) is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutation of a DNA helicase. Among the principal symptoms of the disease are chromosome instability and a propensity to develop cancer. Explain these symptoms on the basis of the helicase mutation.
Problem 25
How does rolling circle replication differ from bidirectional replication?
Problem 26a
Telomeres are found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. What is the sequence composition of telomeres?
Problem 26b
Telomeres are found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. How does telomerase assemble telomeres?
Problem 26c
Telomeres are found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. What is the functional role of telomeres?
Problem 26d
Telomeres are found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. Why is telomerase usually active in germ-line cells but not in somatic cells?
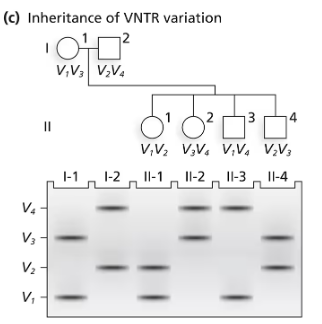
Problem 27a
A family consisting of a mother (I-1), a father (I-2), and three children (II-1, II-2, and II-3) are genotyped by PCR for a region of an autosome containing repeats of a 10-bp sequence. The mother carries 16 repeats on one chromosome and 21 on the homologous chromosome. The father carries repeat numbers of 18 and 26.
Following the layout of the following figure, which aligns members of a pedigree with their DNA fragments in a gel, draw a DNA gel containing the PCR fragments generated by amplification of DNA from the parents (I-1 and I-2). Label the size of each fragment.
Problem 27b
A family consisting of a mother (I-1), a father (I-2), and three children (II-1, II-2, and II-3) are genotyped by PCR for a region of an autosome containing repeats of a 10-bp sequence. The mother carries 16 repeats on one chromosome and 21 on the homologous chromosome. The father carries repeat numbers of 18 and 26.
Identify all the possible genotypes of children of this couple by specifying PCR fragment lengths in each genotype.
Problem 27c
A family consisting of a mother (I-1), a father (I-2), and three children (II-1, II-2, and II-3) are genotyped by PCR for a region of an autosome containing repeats of a 10-bp sequence. The mother carries 16 repeats on one chromosome and 21 on the homologous chromosome. The father carries repeat numbers of 18 and 26.
What genetic term best describes the pattern of inheritance of this DNA marker? Explain your choice.
Problem 28a
In a dideoxy DNA sequencing experiment, four separate reactions are carried out to provide the replicated material for DNA sequencing gels. Reaction products are usually run in gel lanes labeled A, T, C, and G.
Identify the nucleotides used in the dideoxy DNA sequencing reaction that produces molecules for the A lane of the sequencing gel.
Problem 28b
In a dideoxy DNA sequencing experiment, four separate reactions are carried out to provide the replicated material for DNA sequencing gels. Reaction products are usually run in gel lanes labeled A, T, C, and G.
How does PCR play a role in dideoxy DNA sequencing?
Problem 28c
In a dideoxy DNA sequencing experiment, four separate reactions are carried out to provide the replicated material for DNA sequencing gels. Reaction products are usually run in gel lanes labeled A, T, C, and G.
Why is incorporation of a dideoxynucleotide during DNA sequencing identified as a 'replication-terminating' event?
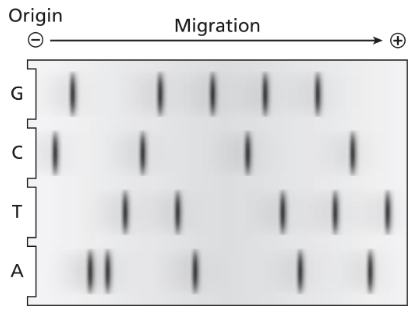
Problem 29
The following dideoxy DNA sequencing gel is produced in a laboratory.
What is the double-stranded DNA sequence of this molecule? Label the polarity of each strand.
Problem 30
Using an illustration style and labeling, draw the electrophoresis gel containing dideoxy sequencing fragments for the DNA template strand 3'-AGACGATAGCAT-5'.
Problem 31
A PCR reaction begins with one double-stranded segment of DNA. How many double-stranded copies of DNA are present after the completion of 10 amplification cycles? After 20 cycles? After 30 cycles?