Back
BackProblem 16
In an assessment of learning in Drosophila, flies were trained to avoid certain olfactory cues. In one population, a mean of 8.5 trials was required. A subgroup of this parental population that was trained most quickly (mean=6.0) was interbred, and their progeny were examined. These flies demonstrated a mean training value of 7.5. Calculate realized heritability for olfactory learning in Drosophila.
Problem 17
Suppose you want to develop a population of Drosophila that would rapidly learn to avoid certain substances the flies could detect by smell. Based on the heritability estimate you obtained in Problem 16, do you think it would be worth doing this by artificial selection? Why or why not?
Problem 18
In a population of tomato plants, mean fruit weight is 60 g and h² is 0.3. Predict the mean weight of the progeny if tomato plants whose fruit averaged 80 g were selected from the original population and interbred.
Problem 19
In a population of 100 inbred, genotypically identical rice plants, variance for grain yield is 4.67. What is the heritability for yield? Would you advise a rice breeder to improve yield in this strain of rice plants by selection?
Problem 20a
Many traits of economic or medical significance are determined by quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in which many genes, usually scattered throughout the genome, contribute to expression.
What general procedures are used to identify such loci?
Problem 20b
Many traits of economic or medical significance are determined by quantitative trait loci (QTLs) in which many genes, usually scattered throughout the genome, contribute to expression.
What is meant by the term cosegregate in the context of QTL mapping? Why are markers such as RFLPs, SNPs, and microsatellites often used in QTL mapping?
Problem 21a
A 3-inch plant was crossed with a 15-inch plant, and all F₁ plants were 9 inches. The F₂ plants exhibited a 'normal distribution,' with heights of 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 inches.
What ratio will constitute the 'normal distribution' in the F₂?
Problem 21b
A 3-inch plant was crossed with a 15-inch plant, and all F₁ plants were 9 inches. The F₂ plants exhibited a 'normal distribution,' with heights of 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, and 15 inches.
What will be the outcome if the F₁ plants are testcrossed with plants that are homozygous for all nonadditive alleles?
Problem 22
In a cross between a strain of large guinea pigs and a strain of small guinea pigs, the F₁ are phenotypically uniform, with an average size about intermediate between that of the two parental strains. Among 1014 F₂ individuals, 3 are about the same size as the small parental strain and 5 are about the same size as the large parental strain. How many gene pairs are involved in the inheritance of size in these strains of guinea pigs?
Problem 23
Type A1B brachydactyly (short middle phalanges) is a genetically determined trait that maps to the short arm of chromosome 5 in humans. If you classify individuals as either having or not having brachydactyly, the trait appears to follow a single-locus, incompletely dominant pattern of inheritance. However, if one examines the fingers and toes of affected individuals, one sees a range of expression from extremely short to only slightly short. What might cause such variation in the expression of brachydactyly?
Problem 24a
In a series of crosses between two true-breeding strains of peaches, the F₁ generation was uniform, producing 30-g peaches. The F₂ fruit mass ranges from 38 to 22 g at intervals of 2 g.
Using these data, determine the number of polygenic loci involved in the inheritance of peach mass.
Problem 24b
In a series of crosses between two true-breeding strains of peaches, the F₁ generation was uniform, producing 30-g peaches. The F₂ fruit mass ranges from 38 to 22 g at intervals of 2 g.
Using gene symbols of your choice, give the genotypes of the parents and the F₂.
Problem 25
Students in a genetics laboratory began an experiment in an attempt to increase heat tolerance in two strains of Drosophila melanogaster. One strain was trapped from the wild six weeks before the experiment was to begin; the other was obtained from a Drosophila repository at a university laboratory. In which strain would you expect to see the most rapid and extensive response to heat-tolerance selection, and why?
Problem 26
Consider a true-breeding plant, AABBCC, crossed with another true-breeding plant, aabbcc, whose resulting offspring are AaBbCc. If you cross the F₁ generation, and independent assortment is operational, the expected fraction of offspring in each phenotypic class is given by the expression N!/M!(N−M)! where N is the total number of alleles (six in this example) and M is the number of uppercase alleles. In a cross of AaBbCc×AaBbCc, what proportion of the offspring would be expected to contain two uppercase alleles?
Problem 27
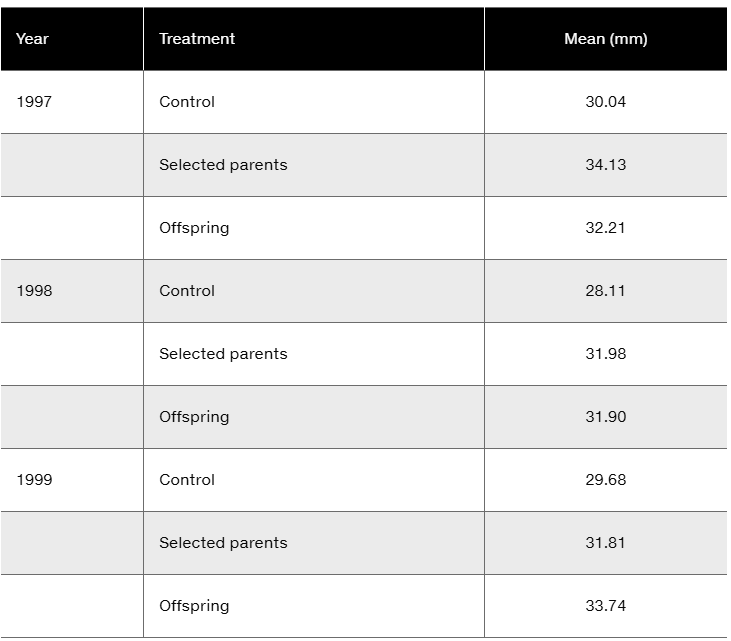
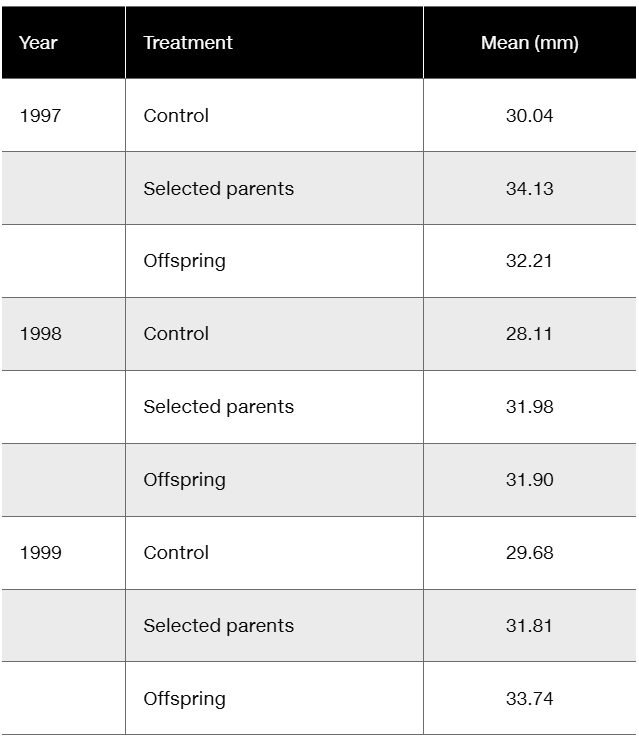
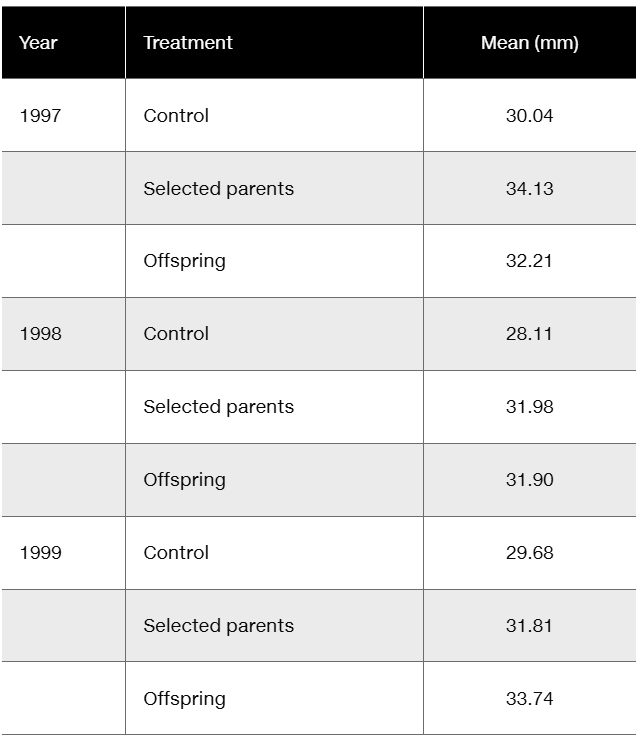
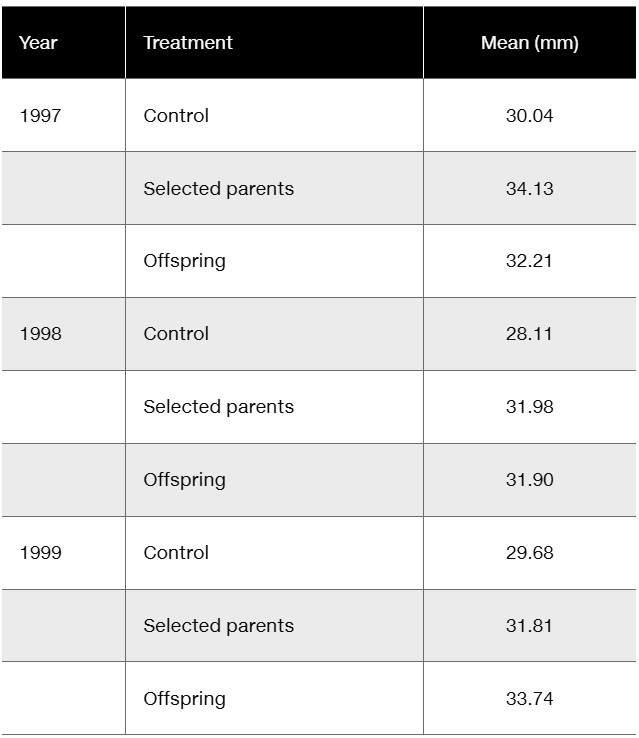
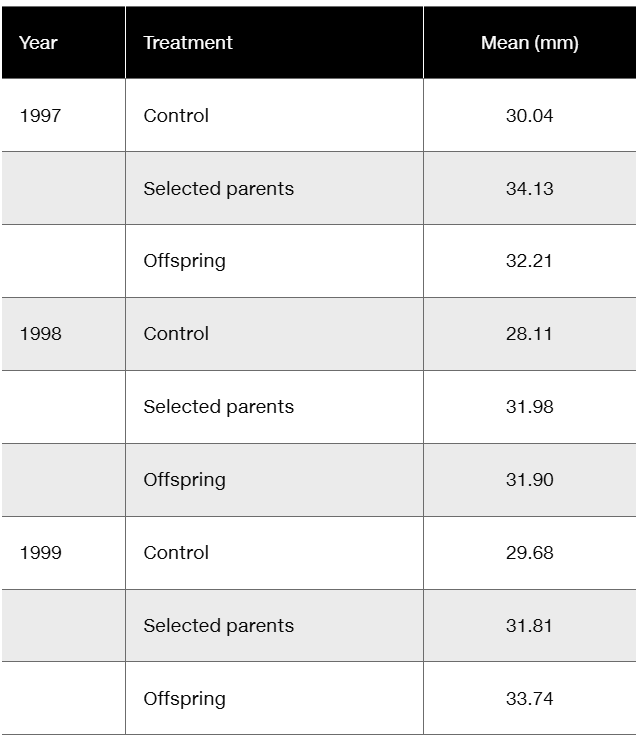
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in a modified form and content.
Considering that differences in control values represent year-to-year differences in greenhouse conditions, calculate (in mm) the average response to selection over the three-year period
Problem 28a
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in modified form and content.
Considering that differences in control values represent year-to-year differences in greenhouse conditions, calculate (in mm) the average response to selection over the three-year period.
Problem 28b
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in modified form and content.
Calculate the realized heritability for each year and the overall realized heritability.
Problem 28c
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in modified form and content.
Assuming that the realized heritability in phlox is relatively high, what factors might account for such a high response?
Problem 28d
Floral traits in plants often play key roles in diversification, in that slight modifications of those traits, if genetically determined, may quickly lead to reproductive restrictions and evolution. Insight into genetic involvement in flower formation is often acquired through selection experiments that expose realized heritability. Lendvai and Levin (2003) conducted a series of artificial selection experiments on flower size (diameter) in Phlox drummondii. Data from their selection experiments are presented in the following table in modified form and content.
In terms of evolutionary potential, is a population with high heritability likely to be favored compared to one with a low realized heritability?
Problem 29a
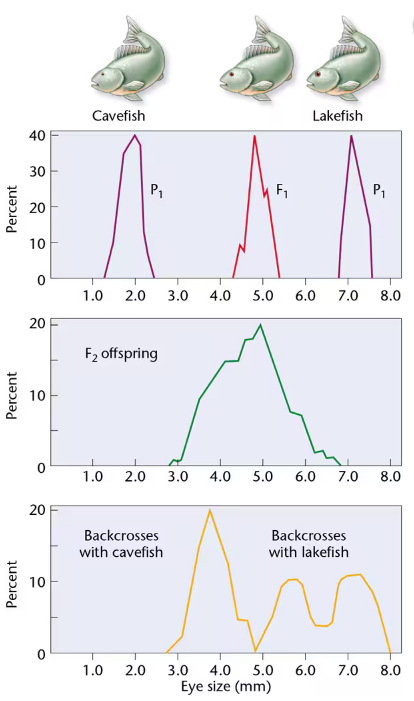
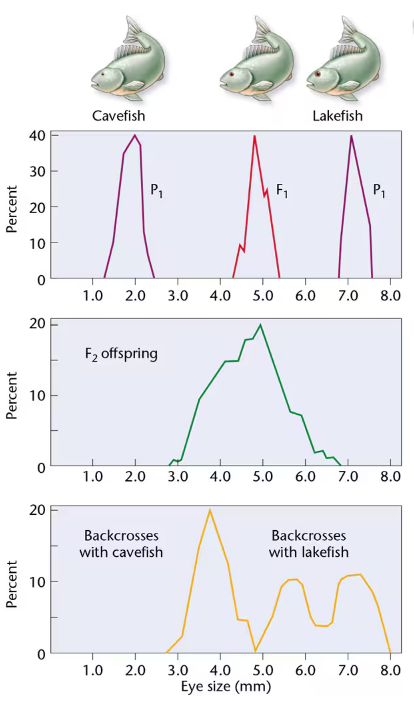
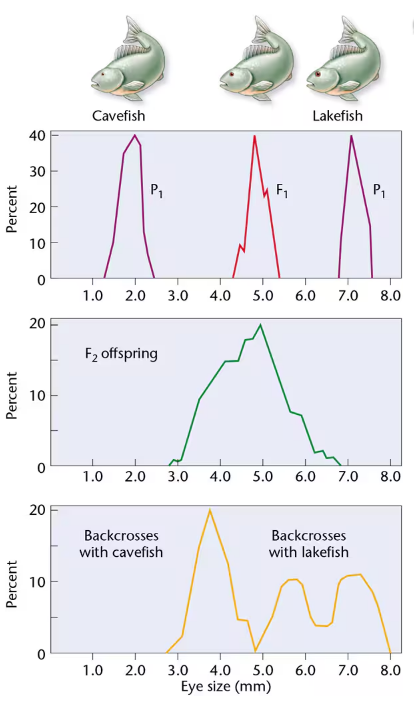
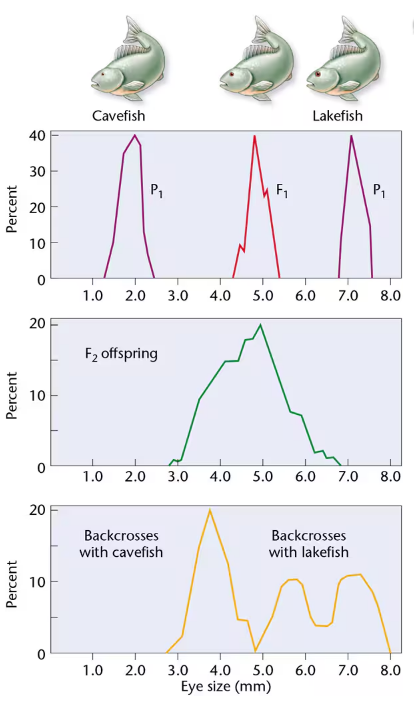
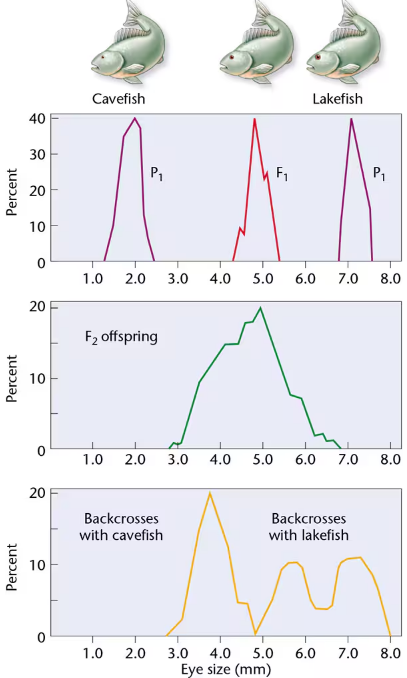
In 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind cavefish, comparing them with members of a sibling species with normal vision that are found in a lake [Wilkens, H. (1988). Evol. Biol. 25:271–367]. We will call them cavefish and lakefish. Wilkens found that cavefish eyes are about seven times smaller than lakefish eyes. F₁ hybrids have eyes of intermediate size. These data, as well as the F₁ × F₁ cross and those from backcrosses (F₁ × cavefish and F₁ × lakefish), are depicted below. Examine Wilkens's results and respond to the following questions:
Based strictly on the F₁ and F₂ results of Wilkens's initial crosses, what possible explanation concerning the inheritance of eye size seems most feasible?
Problem 29b
In 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind cavefish, comparing them with members of a sibling species with normal vision that are found in a lake [Wilkens, H. (1988). Evol. Biol. 25:271–367]. We will call them cavefish and lakefish. Wilkens found that cavefish eyes are about seven times smaller than lakefish eyes. F₁ hybrids have eyes of intermediate size. These data, as well as the F₁×F₁ cross and those from backcrosses (F₁×cavefish and F₁×lakefish), are depicted below. Examine Wilkens's results and respond to the following questions:
Based on the results of the F₁ backcross with cavefish, is your explanation supported? Explain.
Problem 29c
In 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind cavefish, comparing them with members of a sibling species with normal vision that are found in a lake [Wilkens, H. (1988). Evol. Biol. 25:271–367]. We will call them cavefish and lakefish. Wilkens found that cavefish eyes are about seven times smaller than lakefish eyes. F₁ hybrids have eyes of intermediate size. These data, as well as the F₁×F₁ cross and those from backcrosses (F₁×cavefish and F₁×lakefish), are depicted below. Examine Wilkens's results and respond to the following questions:
Based on the results of the F₁ backcross with lakefish, is your explanation supported? Explain.
Problem 29d
In 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind cavefish, comparing them with members of a sibling species with normal vision that are found in a lake [Wilkens, H. (1988). Evol. Biol. 25:271–367]. We will call them cavefish and lakefish. Wilkens found that cavefish eyes are about seven times smaller than lakefish eyes. F₁ hybrids have eyes of intermediate size. These data, as well as the F₁ × F₁ cross and those from backcrosses (F₁ × cavefish and F₁ × lakefish), are depicted below. Examine Wilkens's results and respond to the following questions:
Wilkens examined about 1000 F₂ progeny and estimated that 6–7 genes are involved in determining eye size. Is the sample size adequate to justify this conclusion? Propose an experimental protocol to test the hypothesis.
Problem 29e
In 1988, Horst Wilkens investigated blind cavefish, comparing them with members of a sibling species with normal vision that are found in a lake [Wilkens, H. (1988). Evol. Biol. 25:271–367]. We will call them cavefish and lakefish. Wilkens found that cavefish eyes are about seven times smaller than lakefish eyes. F₁ hybrids have eyes of intermediate size. These data, as well as the F₁ × F₁ cross and those from backcrosses (F₁ × cavefish and F₁ × lakefish), are depicted below. Examine Wilkens's results and respond to the following questions:
A comparison of the embryonic eye in cavefish and lakefish revealed that both reach approximately 4 mm in diameter. However, lakefish eyes continue to grow, while cavefish eye size is greatly reduced. Speculate on the role of the genes involved in this problem.