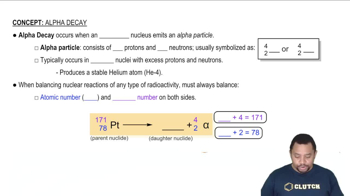
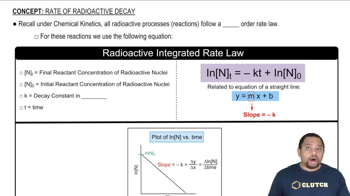
Nuclear Equations
Nuclear equations represent the transformation of one nuclide into another during radioactive decay. They are written to show the initial nuclide, the emitted particles, and the resulting nuclide. For example, in alpha decay, the equation includes the original nuclide, an alpha particle (helium nucleus), and the new nuclide formed after the decay.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance