Two systems, each composed of three particles represented by circles, have 30 J of total energy. How many energetically equivalent ways can you distribute the particles in each system? Which system has greater entropy?
Ch.18 - Free Energy and Thermodynamics

Chapter 18, Problem 33
What is the change in entropy that occurs in the system when 45.0 g of acetone (C3H6O) freezes at its melting point (-94.8 °C)? Use Table 11.9 for the heats of fusion.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the formula for calculating the change in entropy (\( \Delta S \)) during a phase change: \( \Delta S = \frac{q_{\text{rev}}}{T} \), where \( q_{\text{rev}} \) is the heat absorbed or released during the phase change and \( T \) is the temperature in Kelvin.
Convert the given mass of acetone (45.0 g) to moles using its molar mass (58.08 g/mol).
Use the heat of fusion for acetone from Table 11.9 to calculate \( q_{\text{rev}} \). The heat of fusion is the amount of energy required to change a substance from solid to liquid at its melting point.
Convert the temperature from Celsius to Kelvin by adding 273.15 to the given melting point (-94.8 °C).
Substitute the values of \( q_{\text{rev}} \) and \( T \) into the entropy change formula to find \( \Delta S \).
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Entropy
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system. In thermodynamics, it quantifies the number of ways a system can be arranged, with higher entropy indicating greater disorder. When a substance undergoes a phase change, such as freezing, the entropy of the system changes, reflecting the transition from a more disordered state (liquid) to a more ordered state (solid).
Recommended video:
Guided course

Entropy in Thermodynamics
Heats of Fusion
The heat of fusion is the amount of energy required to change a substance from solid to liquid at its melting point, or vice versa. This value is crucial for calculating the energy changes during phase transitions. In the context of freezing, the heat of fusion will be released as the substance transitions from liquid to solid, affecting the overall entropy of the system.
Recommended video:
Guided course
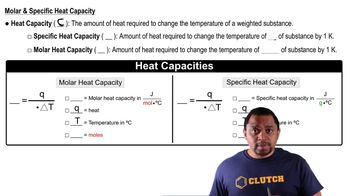
Heat Capacity
Phase Changes
Phase changes refer to the transitions between solid, liquid, and gas states of matter. Each phase has distinct properties and energy levels. When a substance freezes, it undergoes a phase change from liquid to solid, which involves a release of energy and a decrease in entropy, as the molecules become more ordered in the solid state.
Recommended video:
Guided course
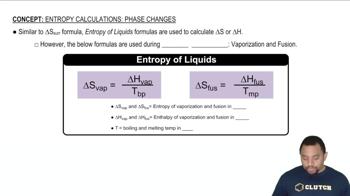
Entropy in Phase Changes
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Calculate the change in entropy that occurs in the system when 1.00 mole of isopropyl alcohol (C3H8O) melts at its melting point (-89.5 °C). See Table 11.9 for heats of fusion.
Textbook Question
Calculate the change in entropy that occurs in the system when 1.00 mole of diethyl ether (C4H10O) condenses from a gas to a liquid at its normal boiling point (34.6 °C). See Table 11.7 for heats of vaporization.
Textbook Question
Without doing any calculations, determine the sign of ΔSsys for each chemical reaction. a. 2 KClO3(s) → 2 KCl(s) + 3 O2(g) c. Na(s) + 2 Cl2(g) → NaCl(s) d. N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → 2 NH3(g)
1
views
Textbook Question
Without doing any calculations, determine the sign of ΔSsys for each chemical reaction. b. CH2=CH2( g) + H2( g) → CH3CH3( g)
