Calculate the change in entropy that occurs in the system when 1.00 mole of diethyl ether (C4H10O) condenses from a gas to a liquid at its normal boiling point (34.6 °C). See Table 11.7 for heats of vaporization.
Ch.18 - Free Energy and Thermodynamics

Chapter 18, Problem 35a,c,d
Without doing any calculations, determine the sign of ΔSsys for each chemical reaction. a. 2 KClO3(s) → 2 KCl(s) + 3 O2(g) c. Na(s) + 2 Cl2(g) → NaCl(s) d. N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → 2 NH3(g)
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the states of matter for each substance in the reaction.
Recognize that entropy (ΔS) is a measure of disorder or randomness in a system.
Note that gases generally have higher entropy than solids due to their greater freedom of movement.
Compare the number of moles of gaseous products to the number of moles of gaseous reactants.
Conclude that if the number of moles of gas increases, ΔS_sys is likely positive, indicating an increase in entropy.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Entropy (ΔS)
Entropy, denoted as ΔS, is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system. In chemical reactions, an increase in the number of gas molecules typically leads to an increase in entropy, while a decrease in the number of gas molecules can result in a decrease in entropy. Understanding how the states of matter and the number of particles change during a reaction is crucial for predicting the sign of ΔS.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Entropy in Thermodynamics
States of Matter
The states of matter—solid, liquid, and gas—play a significant role in determining the entropy of a system. Solids have a fixed structure and lower entropy, while gases have more freedom of movement and higher entropy. In the given reaction, the transition from solid KClO3 to gaseous O2 indicates a change in the state of matter that affects the overall disorder of the system.
Recommended video:
Guided course
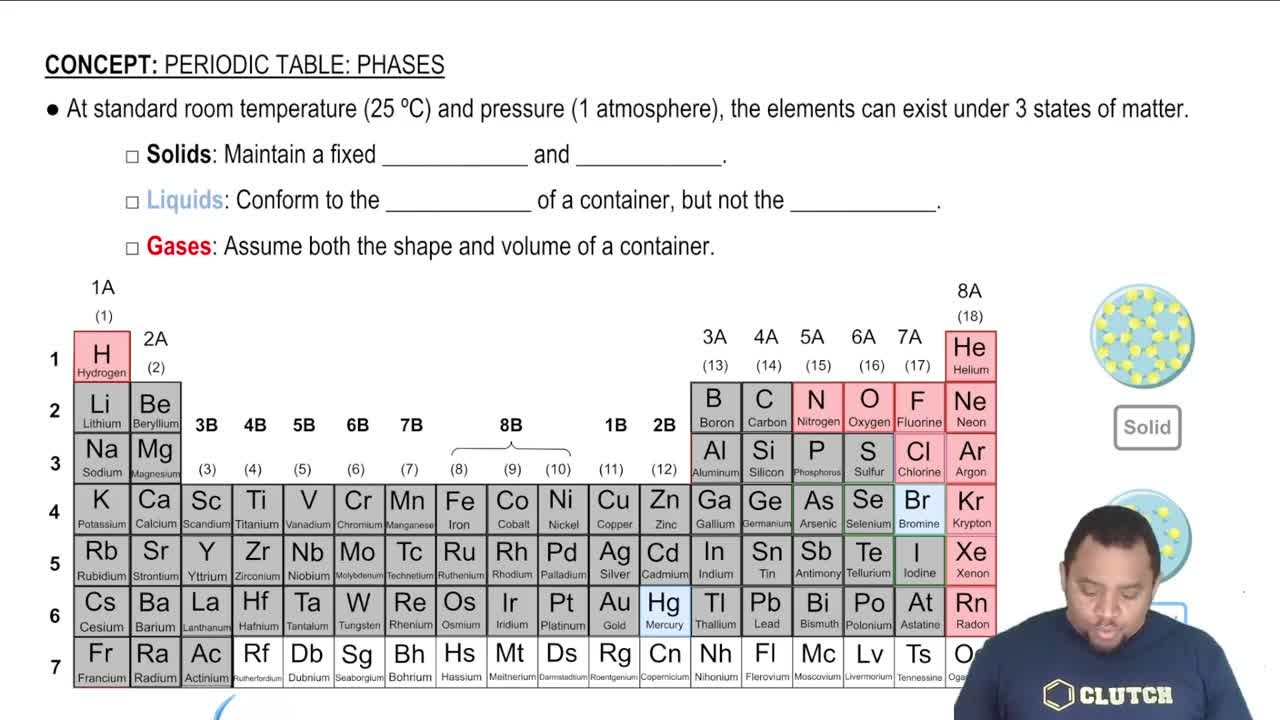
Element States of Matter
Chemical Reaction Stoichiometry
Chemical reaction stoichiometry involves the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. In the provided reaction, the stoichiometry shows that 2 moles of solid KClO3 produce 3 moles of gaseous O2 and 2 moles of solid KCl. This increase in the number of gaseous products relative to the reactants suggests an increase in entropy, which is essential for determining the sign of ΔS.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Stoichiometry Concept
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Without doing any calculations, determine the sign of ΔSsys for each chemical reaction. b. CH2=CH2( g) + H2( g) → CH3CH3( g)
Textbook Question
Without doing any calculations, determine the sign of ΔSsys for each chemical reaction. a. Mg(s) + Cl2(g) → MgCl2(s) b. 2 H2S(g) + 3 O2(g) → 2 H2O(g) + 2 SO2(g) c. 2 O3(g) → 3 O2(g) d. HCl(g) + NH3(g) → NH4Cl(s)
Textbook Question
Without doing any calculations, determine the signs of ΔSsys and ΔS surr for each chemical reaction. In addition, predict under what temperatures (all temperatures, low temperatures, or high temperatures), if any, the reaction is spontaneous. a. C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(g) ΔH°rxn = -2044 kJ
1
views
