Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. b. a solution that is 0.16 M in NH3 and 0.22 M in NH4Cl

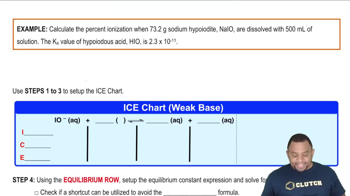
What is the percent ionization of a 0.13 M formic acid solution in pure water, and how does it compare to the percent ionization in a solution containing 0.11 M potassium formate?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Ionization of Weak Acids

Percent Ionization
Common Ion Effect
Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. a. a solution that is 0.195 M in HC2H3O2 and 0.125 M in KC2H3O2 b. a solution that is 0.255 M in CH3NH2 and 0.135 M in CH3NH3Br
Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.15 M benzoic acid solution in pure water and in a solution containing 0.10 M sodium benzoate. Why does the percent ionization differ significantly in the two solutions?
Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. a. 0.15 M HF
Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. b. 0.15 M NaF
Solve an equilibrium problem (using an ICE table) to calculate the pH of each solution. c. a mixture that is 0.15 M in HF and 0.15 M in NaF
