Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. a. 75.0 mL of 0.10 M HF; 55.0 mL of 0.15 M NaF b. 150.0 mL of 0.10 M HF; 135.0 mL of 0.175 M HCl d. 125.0 mL of 0.15 M CH3NH2; 120.0 mL of 0.25 M CH3NH3Cl
Ch.17 - Aqueous Ionic Equilibrium

Chapter 17, Problem 55a
Blood is buffered by carbonic acid and the bicarbonate ion. Normal blood plasma is 0.024 M in HCO3- and 0.0012 M H2CO3 (pKa1 for H2CO3 at body temperature is 6.1).
a. What is the pH of blood plasma?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the components of the buffer system: carbonic acid (H_2CO_3) and bicarbonate ion (HCO_3^-).
Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for buffer solutions: \( \text{pH} = \text{pK}_a + \log \left( \frac{[\text{A}^-]}{[\text{HA}]} \right) \), where \([\text{A}^-]\) is the concentration of the base (HCO_3^-) and \([\text{HA}]\) is the concentration of the acid (H_2CO_3).
Substitute the given concentrations into the equation: \([\text{A}^-] = 0.024 \text{ M}\) and \([\text{HA}] = 0.0012 \text{ M}\).
Substitute the given \(\text{pK}_a\) value into the equation: \(\text{pK}_a = 6.1\).
Calculate the pH using the equation: \( \text{pH} = 6.1 + \log \left( \frac{0.024}{0.0012} \right) \).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Buffer Systems
Buffer systems are solutions that resist changes in pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid or base. In biological systems, buffers maintain the pH within a narrow range, which is crucial for proper physiological function. The bicarbonate buffer system, involving carbonic acid (H2CO3) and bicarbonate ion (HCO3-), is particularly important in regulating blood pH.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Buffer Capacity
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation relates the pH of a buffer solution to the concentration of its acidic and basic components. It is expressed as pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]), where [A-] is the concentration of the base (bicarbonate) and [HA] is the concentration of the acid (carbonic acid). This equation is essential for calculating the pH of buffered solutions, such as blood plasma.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
pKa and Acid-Base Equilibrium
pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) and indicates the strength of an acid in solution. A lower pKa value signifies a stronger acid that dissociates more readily. In the context of the bicarbonate buffer system, the pKa of carbonic acid (6.1) helps determine the pH of blood plasma by indicating the equilibrium between carbonic acid and bicarbonate ions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
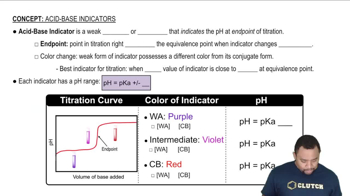
Acid-Base Indicators
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. c. 165.0 mL of 0.10 M HF; 135.0 mL of 0.050 M KOH
1
views
Textbook Question
Determine whether or not the mixing of each pair of solutions results in a buffer. e. 105.0 mL of 0.15 M CH3NH2; 95.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl
1
views
Textbook Question
Blood is buffered by carbonic acid and the bicarbonate ion. Normal blood plasma is 0.024 M in HCO3- and 0.0012 M H2CO3 (pKa1 for H2CO3 at body temperature is 6.1).
c. Given the volume from part (b), what mass of NaOH can be neutralized before the pH rises above 7.8?
Textbook Question
The fluids within cells are buffered by H2PO4- and HPO42- . b. Could a buffer system employing H3PO4 as the weak acid and H2PO4- as the weak base be used as a buffer system within cells? Explain.
1
views
