This reaction was monitored as a function of time: A → B + C A plot of ln[A] versus time yields a straight line with slope -0.0045/s. b. Write the rate law for the reaction.

This reaction was monitored as a function of time: AB → A + B A plot of 1/[AB] versus time yields a straight line with a slope of +0.55/Ms.
a. What is the value of the rate constant (k) for this reaction at this temperature?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
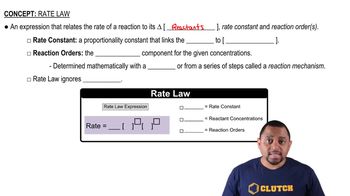
Rate Law
Integrated Rate Laws

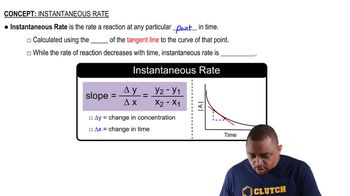
Slope of a Line
This reaction was monitored as a function of time: A → B + C A plot of ln[A] versus time yields a straight line with slope -0.0045/s. c. What is the half-life?
This reaction was monitored as a function of time: A → B + C A plot of ln[A] versus time yields a straight line with slope -0.0045/s. d. If the initial concentration of A is 0.250 M, what is the concentration after 225 s?
This reaction was monitored as a function of time: AB → A + B A plot of 1/[AB] versus time yields a straight line with a slope of +0.55/Ms. b. Write the rate law for the reaction.
This reaction was monitored as a function of time: AB → A + B A plot of 1/[AB] versus time yields a straight line with a slope of +0.55/Ms. c. What is the half-life when the initial concentration is 0.55 M?
This reaction was monitored as a function of time: AB → A + B A plot of 1/[AB] versus time yields a straight line with a slope of +0.55/Ms.
d. If the initial concentration of AB is 0.250 M, and the reaction mixture initially contains no products, what are the concentrations of A and B after 75 s?
