Consider the reaction: H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2 HBr(g) The graph shows the concentration of Br2 as a function of time. a. Use the graph to calculate each quantity: (iii) the instantaneous rate of formation of HBr at 50 s

Consider the reaction: 2 H2O2(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + O2(g). The graph shows the concentration of H2O2 as a function of time. Use the graph to calculate each quantity: a. the average rate of the reaction between 10 and 20 seconds, b. the instantaneous rate of the reaction at 30 seconds.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Reaction Rate
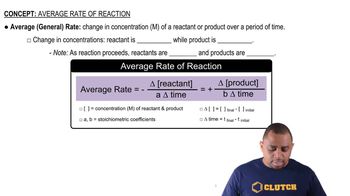
Average Rate of Reaction

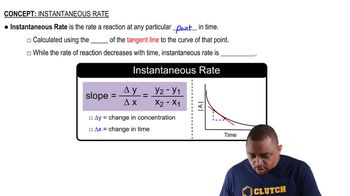
Instantaneous Rate of Reaction
Consider the reaction: H2( g) + Br2( g) → 2 HBr( g) The graph shows the concentration of Br2 as a function of time.
b. Make a rough sketch of a curve representing the concentration of HBr as a function of time. Assume that the initial concentration of HBr is zero
Consider the reaction: 2 H2O2(aq) → 2 H2O(l ) + O2( g) The graph shows the concentration of H2O2 as a function of time.
Use the graph to calculate each quantity: c. the instantaneous rate of formation of O2 at 50 s
Consider the reaction: 2 H2O2(aq) → 2 H2O(l ) + O2( g) The graph shows the concentration of H2O2 as a function of time. Use the graph to calculate each quantity: d. If the initial volume of the H2O2 is 1.5 L, what total amount of O2 (in moles) is formed in the first 50 s of reaction?
This graph shows a plot of the rate of a reaction versus the concentration of the reactant A for the reaction A → products. a. What is the order of the reaction with respect to A?
