Consider the reaction: H2(g) + Br2(g) → 2 HBr(g) The graph shows the concentration of Br2 as a function of time. a. Use the graph to calculate each quantity: (iii) the instantaneous rate of formation of HBr at 50 s

Consider the reaction: 2 H2O2(aq) → 2 H2O(l ) + O2( g) The graph shows the concentration of H2O2 as a function of time.
Use the graph to calculate each quantity: c. the instantaneous rate of formation of O2 at 50 s
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
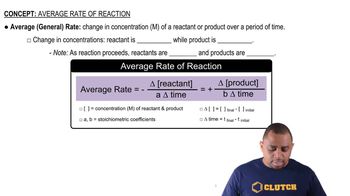
Reaction Rate
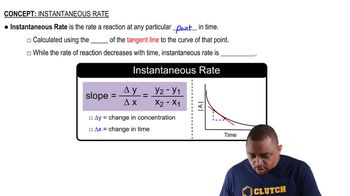
Instantaneous Rate
Stoichiometry

Consider the reaction: H2( g) + Br2( g) → 2 HBr( g) The graph shows the concentration of Br2 as a function of time.
b. Make a rough sketch of a curve representing the concentration of HBr as a function of time. Assume that the initial concentration of HBr is zero
Consider the reaction: 2 H2O2(aq) → 2 H2O(l ) + O2( g) The graph shows the concentration of H2O2 as a function of time. Use the graph to calculate each quantity: d. If the initial volume of the H2O2 is 1.5 L, what total amount of O2 (in moles) is formed in the first 50 s of reaction?
This graph shows a plot of the rate of a reaction versus the concentration of the reactant A for the reaction A → products. a. What is the order of the reaction with respect to A?
This graph shows a plot of the rate of a reaction versus the concentration of the reactant A for the reaction A → products. c. Write a rate law for the reaction including an estimate for the value of k.
