Magnesium citrate, Mg3(C6H5O7)2, belongs to a class of laxatives called hyperosmotics, which cause rapid emptying of the bowel. When a concentrated solution of magnesium citrate is consumed, it passes through the intestines, drawing water and promoting diarrhea, usually within 6 hours. Calculate the osmotic pressure of a magnesium citrate laxative solution containing 28.5 g of magnesium citrate in 235 mL of solution at 37 °C (approximate body temperature). Assume complete dissociation of the ionic compound.
Ch.13 - Solutions

Chapter 13, Problem 111
An isotonic solution contains 0.90% NaCl mass to volume. Calculate the percent mass to volume for isotonic solutions containing each solute at 25 °C. Assume a van't Hoff factor of 1.9 for all ionic solutes. a. KCl
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the van't Hoff factor (i) for KCl, which is given as 1.9. This factor indicates the number of particles the compound dissociates into in solution.
Recognize that the isotonic condition means the osmotic pressures of the solutions must be equal. Since the osmotic pressure is proportional to the concentration of particles in solution, we use the van't Hoff factor to adjust the concentration of KCl to match that of NaCl.
Calculate the effective concentration of particles for NaCl using its van't Hoff factor (which is also 1.9 for this example) and its concentration. The formula to use is: \(i \times C\), where \(C\) is the concentration of NaCl (0.90% m/v).
Set the effective concentration of particles for KCl equal to that of NaCl to maintain isotonicity. Use the formula: \(1.9 \times [KCl]\) = effective concentration of NaCl particles.
Solve for the concentration of KCl, \([KCl]\), that would make the KCl solution isotonic with the NaCl solution. This will give you the percent mass to volume for the isotonic KCl solution.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isotonic Solutions
An isotonic solution has the same osmotic pressure as another solution, typically physiological saline (0.90% NaCl). This means that the concentration of solutes is balanced, preventing net movement of water across cell membranes, which is crucial for maintaining cell integrity and function.
Recommended video:
Guided course
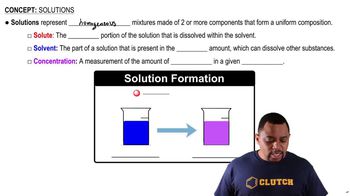
Solution Components
Van't Hoff Factor (i)
The van't Hoff factor (i) indicates the number of particles a solute dissociates into in solution. For ionic compounds like KCl, which dissociates into K+ and Cl-, the van't Hoff factor is 2. However, in this case, a factor of 1.9 is used, accounting for ion pairing in solution, which affects colligative properties.
Recommended video:
Guided course
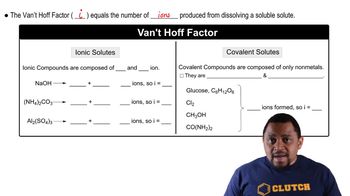
Van't Hoff Factor
Percent Mass to Volume Concentration
Percent mass to volume concentration is a way to express the concentration of a solution, calculated as the mass of solute divided by the volume of solution, multiplied by 100. This measurement is essential for preparing solutions with specific osmotic properties, such as isotonic solutions, to ensure proper physiological function.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mass Percent Calculation
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
When HNO2 is dissolved in water, it partially dissociates according to the equation HNO2 ⇌ H+ + NO2-. A solution is prepared that contains 7.050 g of HNO2 in 1.000 kg of water. Its freezing point is -0.2929 °C. Calculate the fraction of HNO2 that has dissociated.
1
views
