Determine whether each pair of compounds forms a homogeneous solution when combined. For those that form homogeneous solutions, indicate the type of forces that are involved. a. CCl4 and H2O b. KCl and H2O c. Br2 and CCl4
Ch.11 - Liquids, Solids & Intermolecular Forces

Chapter 11, Problem 47
Which compound would you expect to have greater surface tension: acetone [(CH3)2CO] or water (H2O)? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the intermolecular forces present in each compound. Acetone has dipole-dipole interactions and London dispersion forces, while water has hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces.
Understand that surface tension is influenced by the strength of intermolecular forces. Stronger intermolecular forces result in higher surface tension.
Recognize that hydrogen bonding is a particularly strong type of intermolecular force, which is present in water but not in acetone.
Compare the overall strength of intermolecular forces in acetone and water. Water's hydrogen bonds make its intermolecular forces stronger than those in acetone.
Conclude that water, with its stronger intermolecular forces due to hydrogen bonding, would have a greater surface tension compared to acetone.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
59sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Surface Tension
Surface tension is a physical property of liquids that describes the elastic-like force at the surface of a liquid. It arises from the cohesive forces between liquid molecules, which are stronger at the surface due to the lack of neighboring molecules above. This phenomenon causes the surface to behave like a stretched elastic membrane, influencing how liquids interact with solids and other liquids.
Recommended video:
Guided course
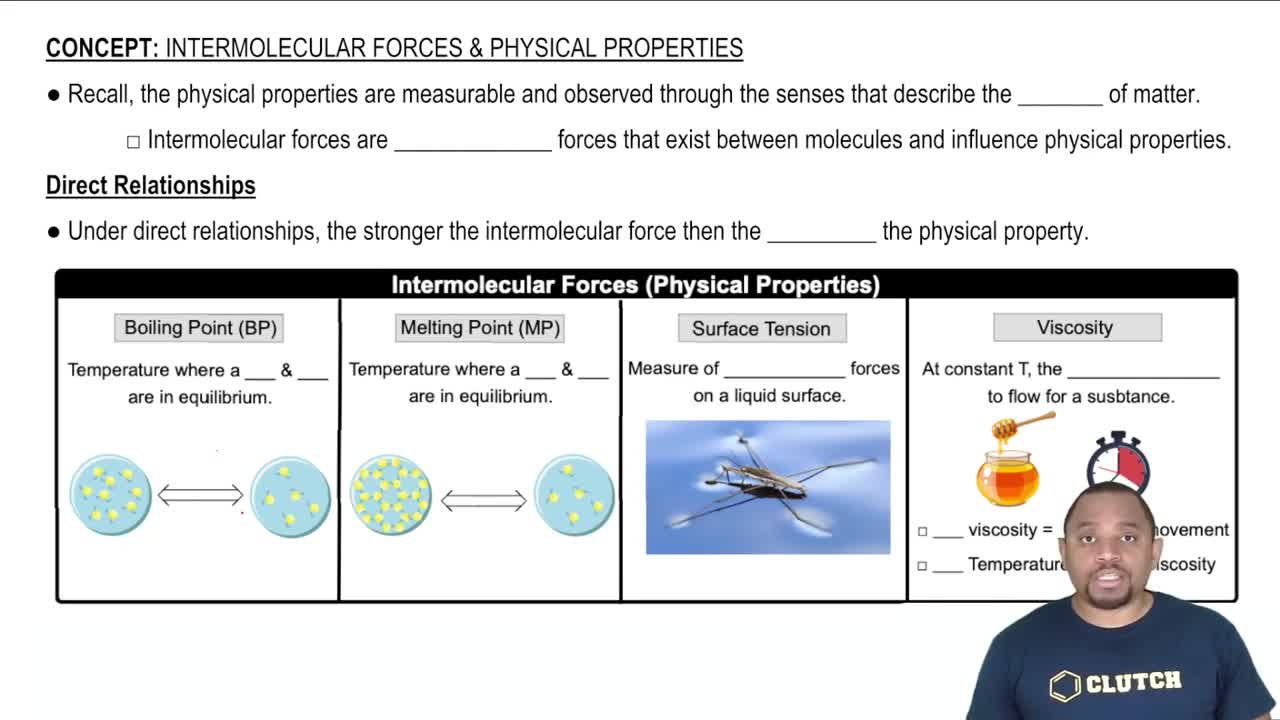
Intermolecular Forces and Properties
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is a type of strong intermolecular attraction that occurs when hydrogen is covalently bonded to highly electronegative atoms like oxygen or nitrogen. In water (H2O), each molecule can form up to four hydrogen bonds with neighboring molecules, leading to a highly structured network. This strong bonding significantly contributes to water's high surface tension compared to many other liquids.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Hydrogenation Reactions
Molecular Structure and Polarity
The molecular structure and polarity of a compound greatly influence its physical properties, including surface tension. Water is a polar molecule, meaning it has a partial positive charge on one side and a partial negative charge on the other, allowing for strong intermolecular attractions. In contrast, acetone [(CH3)2CO] is less polar and has weaker intermolecular forces, resulting in lower surface tension compared to water.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molecular Polarity
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Determine whether each pair of compounds forms a homogeneous solution when combined. For those that form homogeneous solutions, indicate the type of forces that are involved. d. CH3CH2OH and H2O
Textbook Question
Determine whether each pair of compounds forms a homogeneous solution when combined. For those that form homogeneous solutions, indicate the type of forces that are involved. a. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 and CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 b. CBr4 and H2O c. LiNO3 and H2O d. CH3OH and CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
Textbook Question
The structures of two isomers of heptane are shown. Which of these two compounds would you expect to have the greater viscosity?
Textbook Question
Explain why the viscosity of multigrade motor oils is less temperature-dependent than that of single-grade motor oils.
