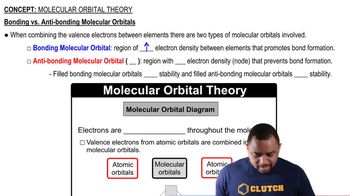
Textbook Question
Look at the MO diagrams of corresponding neutral diatomic species in Figure 8.22, and predict whether each of the following ions is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Diagrams for Li2 and C2 are similar to N2; Cl2 is similar to F2. (c) F2-