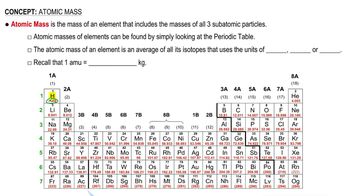
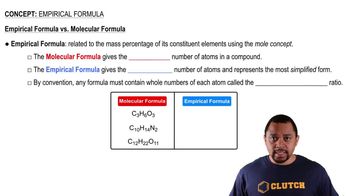
Textbook Question
The stimulant amphetamine contains only carbon, hydrogen, and nitrogen. Combustion analysis of a 42.92 mg sample of amphetamine gives 37.187 mg of H2O and 125.75 mg of CO2. If the molar mass of amphetamine is less than 160 g/mol, what is its molecular formula?