Textbook Question
Disilane, Si2Hx, is analyzed and found to contain 90.28% silicon by mass. What is the value of x?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

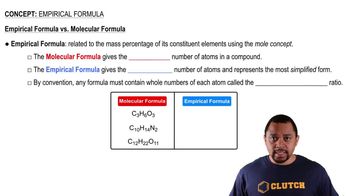
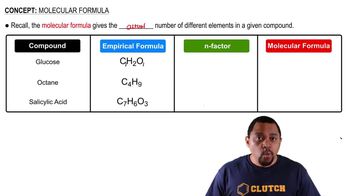
Heating elemental cesium and platinum together for two days at 973 K gives a dark red ionic compound that is 57.67% Cs and 42.33% Pt. (a) What is the empirical formula of the compound?