Textbook Question
Combustion analysis of a 31.472 mg sample of the widely used flame retardant Decabrom gave 1.444 mg of CO2. Is the molecular formula of Decabrom C12Br10 or C12Br10O?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance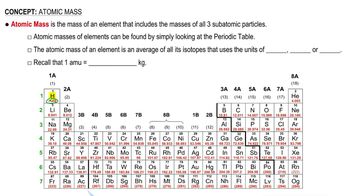
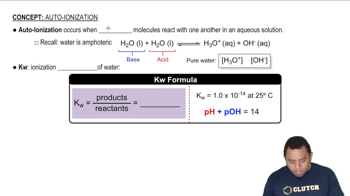
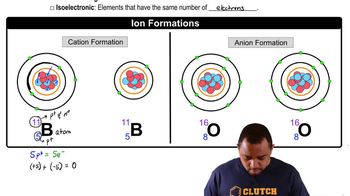
Heating elemental cesium and platinum together for two days at 973 K gives a dark red ionic compound that is 57.67% Cs and 42.33% Pt. (a) What is the empirical formula of the compound?