Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 114
What amino acids do the following abbreviations stand for? (a) Ser (b) Thr (c) Pro (d) Phe (e) Cys
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Recognize that amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and each has a standard three-letter abbreviation.
Step 2: Identify the amino acid for the abbreviation 'Ser'. 'Ser' stands for Serine, which is a polar amino acid with a hydroxyl group in its side chain.
Step 3: Identify the amino acid for the abbreviation 'Thr'. 'Thr' stands for Threonine, another polar amino acid with a hydroxyl group in its side chain.
Step 4: Identify the amino acid for the abbreviation 'Pro'. 'Pro' stands for Proline, which is unique due to its cyclic structure that affects protein folding.
Step 5: Identify the amino acid for the abbreviation 'Phe'. 'Phe' stands for Phenylalanine, a nonpolar amino acid with an aromatic side chain.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid consists of a central carbon atom, an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group) that determines its unique properties. There are 20 standard amino acids, each with a specific three-letter abbreviation and one-letter code.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Binary Acids
Abbreviations of Amino Acids
Amino acids are commonly represented by three-letter and one-letter abbreviations for convenience in scientific communication. For example, 'Ser' stands for serine, 'Thr' for threonine, 'Pro' for proline, 'Phe' for phenylalanine, and 'Cys' for cysteine. Understanding these abbreviations is essential for interpreting protein sequences and structures.
Recommended video:
Guided course
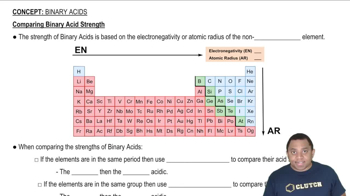
Comparing Binary Acid Strength
Protein Structure and Function
The sequence and composition of amino acids in a protein determine its structure and function. Proteins are essential for various biological processes, including catalyzing reactions, providing structural support, and regulating cellular activities. The specific properties of amino acids, such as polarity and charge, influence how proteins fold and interact with other molecules.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Functional Groups Example
Related Practice
