Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 95
One of the constituents of the carnauba wax used in floor and furniture polish is an ester of a C32 straight-chain alcohol with a C20 straight-chain carboxylic acid. Draw the structure of this ester.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the structure of an ester. An ester is formed from the reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, where the hydroxyl group (OH) of the acid is replaced by an alkoxy group (O-R) from the alcohol.
Step 2: Identify the components involved. In this problem, the ester is formed from a C32 straight-chain alcohol and a C20 straight-chain carboxylic acid.
Step 3: Draw the structure of the C32 straight-chain alcohol. This will be a linear chain of 32 carbon atoms with a hydroxyl group (OH) at one end.
Step 4: Draw the structure of the C20 straight-chain carboxylic acid. This will be a linear chain of 20 carbon atoms with a carboxyl group (COOH) at one end.
Step 5: Combine the structures to form the ester. Remove the hydroxyl group from the carboxylic acid and the hydrogen from the alcohol's hydroxyl group, then connect the oxygen of the alcohol to the carbonyl carbon of the acid to form the ester linkage (R-COO-R').
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ester Formation
Ester formation occurs through a condensation reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, resulting in the release of water. In this process, the hydroxyl group (-OH) from the acid and a hydrogen atom from the alcohol combine to form water, while the remaining parts of the molecules bond to create the ester. Understanding this reaction is crucial for drawing the structure of the ester in the question.
Recommended video:
Guided course
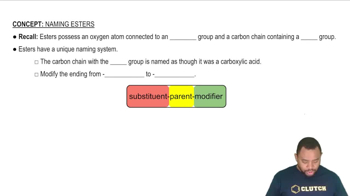
Rules for Naming Esters
Structural Representation of Organic Compounds
Organic compounds, such as esters, can be represented using structural formulas that depict the arrangement of atoms. In the case of the ester mentioned, it is important to illustrate the long carbon chains of the alcohol and carboxylic acid accurately. Familiarity with drawing structural formulas, including line-angle representations, is essential for visualizing the molecular structure.
Recommended video:
Guided course
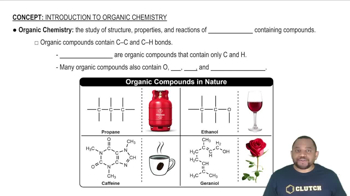
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Chain Length and Functional Groups
The properties and reactivity of organic compounds are significantly influenced by the length of their carbon chains and the presence of functional groups. In this question, the C32 straight-chain alcohol and C20 straight-chain carboxylic acid indicate long carbon chains, which can affect the physical properties of the resulting ester. Recognizing how chain length and functional groups interact is vital for understanding the characteristics of the ester formed.
Recommended video:
Guided course
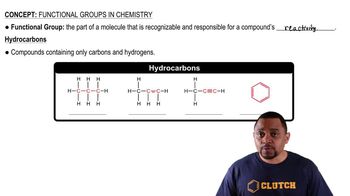
Hydrocarbon Functional Groups
Related Practice
