Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 115
Name and draw the structures of amino acids that fit the following descriptions. (a) Contains an isopropyl group (b) Contains an alcohol group (c) Contains a thiol group (d) Contains an aromatic ring
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the amino acid with an isopropyl group: The isopropyl group is a branched alkyl group with the formula \( \text{C}_3\text{H}_7 \). The amino acid with this side chain is valine. Draw the structure of valine, showing the isopropyl group attached to the central carbon.
Identify the amino acid with an alcohol group: An alcohol group is characterized by the presence of an \( \text{-OH} \) group. The amino acid with an alcohol group is serine. Draw the structure of serine, highlighting the \( \text{-OH} \) group in its side chain.
Identify the amino acid with a thiol group: A thiol group contains a sulfur atom bonded to a hydrogen atom (\( \text{-SH} \)). The amino acid with a thiol group is cysteine. Draw the structure of cysteine, emphasizing the \( \text{-SH} \) group in its side chain.
Identify the amino acid with an aromatic ring: An aromatic ring is a cyclic, planar structure with delocalized electrons. The amino acid with an aromatic ring is phenylalanine. Draw the structure of phenylalanine, showing the benzene ring as part of its side chain.
Review the structures: Ensure that each amino acid structure includes the central \( \alpha \)-carbon, the amino group (\( \text{-NH}_2 \)), the carboxyl group (\( \text{-COOH} \)), and the specific side chain that matches the given description.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Amino Acid Structure
Amino acids are organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins. Each amino acid has a central carbon atom (the alpha carbon) bonded to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain (R group) that determines the amino acid's properties. Understanding the general structure of amino acids is essential for identifying specific types based on their side chains.
Recommended video:
Guided course
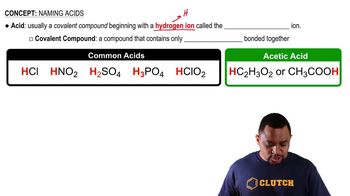
Acids and Their Structure
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. In the context of amino acids, groups such as isopropyl (a branched alkyl group), alcohol (hydroxyl group -OH), thiol (sulfhydryl group -SH), and aromatic rings (cyclic compounds with alternating double bonds) play crucial roles in determining the amino acid's properties and reactivity.
Recommended video:
Guided course
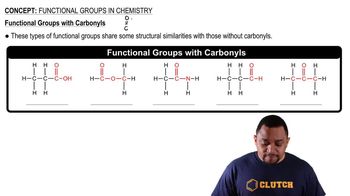
Carbonyl Functional Groups
Amino Acid Classification
Amino acids can be classified based on the properties of their side chains, which can be polar, nonpolar, acidic, or basic. This classification helps in understanding their behavior in biological systems. For example, amino acids with nonpolar side chains, like those containing isopropyl groups, are typically hydrophobic, while those with alcohol or thiol groups are more hydrophilic, influencing protein structure and function.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Ligand Classification
Related Practice
